추천 제품
생물학적 소스
hamster (Syrian)
Quality Level
항체 형태
culture supernatant
항체 생산 유형
primary antibodies
클론
8G10, monoclonal
종 반응성
mouse, rat
제조업체/상표
Chemicon®
기술
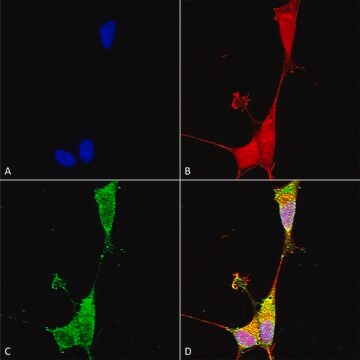
flow cytometry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
동형
IgG1
NCBI 수납 번호
UniProt 수납 번호
배송 상태
wet ice
타겟 번역 후 변형
unmodified
유전자 정보
human ... NOTCH1(4851)
관련 카테고리
일반 설명
Notch 1 is a type 1 membrane protein that serves as a receptor for the membrane bound ligands jagged-1 and -2 and delta-1 to regulate cell fate determination through the implementation of differentiation, proliferation and apoptotic programs. Upon ligand binding, the Notch intracellular domain (NICD) is released by proteolytic processing and subsequently translocates to the nucleus where it forms a transcriptionally active complex with RBP-J kappa to activate genes of the enhancer of split locus. Notch-1 may also be involved in cell specification and/or differentiation and body segment determination in the postimplantation embryo. In the adult animal, Notch-1 is highly expressed in the brain, lung, and thymus with lower expression levels in the spleen, bone-marrow, spinal cord, eyes, mammary gland, liver, intestine, skeletal muscle, kidney and heart.
특이성
Reacts with natural and recombinant Notch1. Recognizes a band migrating at approximately 300 kDa on Western blots of rat and mouse protein extracts. A cross reactive band migrating at approximately 230 kDa is observed in some samples and is believed to correspond to the processed extracellular fragment of Notch 1.
면역원
A GST fusion protein comprising amino acids 1299-1492 of mouse Notch 1
Epitope: extracellular
애플리케이션
Research Category
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Research Sub Category
Transcription Factors
Transcription Factors
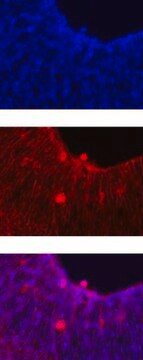
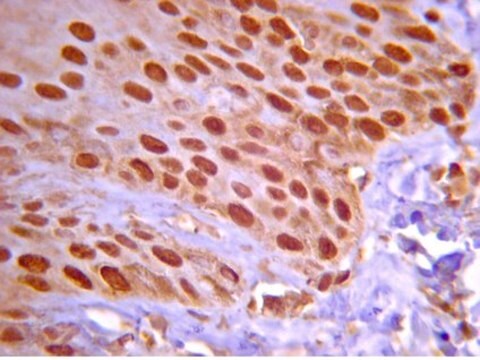
Use Anti-Notch 1 Antibody, extracellular, clone 8G10 (Syrian Hamster Monoclonal Antibody) validated in FC, WB, IHC to detect Notch 1 also known as Motch A, mT14, p300.
Western blot
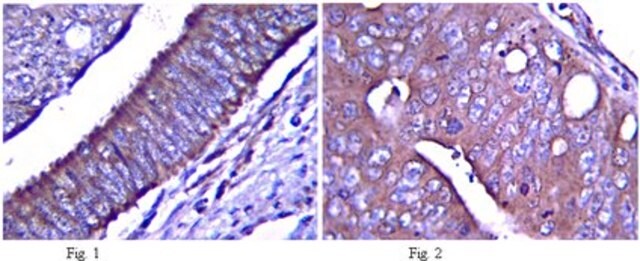
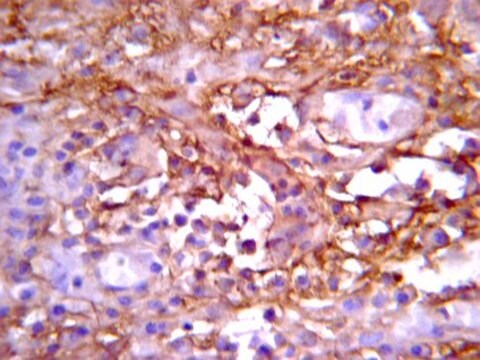
Immunohistochemistry on paraformaldehyde fixed frozen tissue sections.
Flow Cytometry
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Immunohistochemistry on paraformaldehyde fixed frozen tissue sections.
Flow Cytometry
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
결합
Replaces: 04-1046
물리적 형태
Unpurified tissue culture supernatant from a perfusion system, filtered through a 0.2 micron membrane prior to vialing. Product contains 20% FBS and Ciprofloxacin at final concentration of 10 μg/mL.
저장 및 안정성
Maintain at -20°C in undiluted aliquots for up to 6 months from date of receipt. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
분석 메모
Control
POSITIVE CONTROL: brain, lung, thymus.
POSITIVE CONTROL: brain, lung, thymus.
법적 정보
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
면책조항
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
적합한 제품을 찾을 수 없으신가요?
당사의 제품 선택기 도구.을(를) 시도해 보세요.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
시험 성적서(COA)
제품의 로트/배치 번호를 입력하여 시험 성적서(COA)을 검색하십시오. 로트 및 배치 번호는 제품 라벨에 있는 ‘로트’ 또는 ‘배치’라는 용어 뒤에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
Paschalis Kratsios et al.
Circulation research, 106(3), 559-572 (2009-12-17)
The Notch signaling pathway is important for cell-cell communication that controls tissue formation and homeostasis during embryonic and adult life, but the precise cell targets of Notch signaling in the mammalian heart remain poorly defined. To investigate the functional role
Notch in vertebrates
Robey, E.
Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 7, 551-557 (1997)
Distinct TCR signaling pathways drive proliferation and cytokine production in T cells.
Guy, CS; Vignali, KM; Temirov, J; Bettini, ML; Overacre, AE; Smeltzer, M; Zhang, H; Huppa et al.
Nature Immunology null
Donna Nichol et al.
Blood, 116(26), 6133-6143 (2010-10-16)
Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 (Egfl7) is important for regulating tubulogenesis in zebrafish, but its role in mammals remains unresolved. We show here that endothelial overexpression of Egfl7 in transgenic mice leads to partial lethality, hemorrhaging, and altered cardiac morphogenesis.
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.