추천 제품
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
애플리케이션
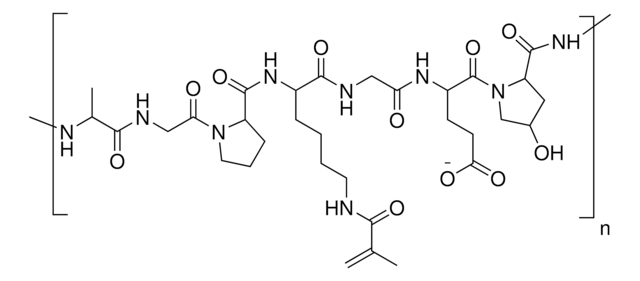
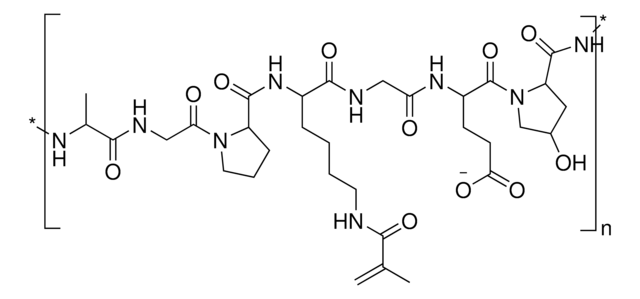
This product is low endotoxin version GelMA and ready to be used in biomedical applications. The bloom number is ∼170.
GelMA can be used to form hydrogels for tissue engineering and 3D bioprinting. Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) is a polymerizable hydrogel material derived from natural extracellular matrix (ECM) components. Due to its low cost, abundance, and retention of natural cell binding motifs, gelatin has become a highly sought material for tissue engineering applications. The addition of photocrosslinkable methacrylamide functional groups in GelMA allows the synthesis of biocompatible, biodegradable, and non-immunogenic hydrogels that are stable in biologically relevant conditions and promote cell adhesion, spreading, and proliferation.
GelMA can be used to form hydrogels for tissue engineering and 3D bioprinting. Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) is a polymerizable hydrogel material derived from natural extracellular matrix (ECM) components. Due to its low cost, abundance, and retention of natural cell binding motifs, gelatin has become a highly sought material for tissue engineering applications. The addition of photocrosslinkable methacrylamide functional groups in GelMA allows the synthesis of biocompatible, biodegradable, and non-immunogenic hydrogels that are stable in biologically relevant conditions and promote cell adhesion, spreading, and proliferation.
포장
1g in bottle
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
Xin Zhao et al.
Advanced healthcare materials, 5(1), 108-118 (2015-04-17)
Natural hydrogels are promising scaffolds to engineer epidermis. Currently, natural hydrogels used to support epidermal regeneration are mainly collagen- or gelatin-based, which mimic the natural dermal extracellular matrix but often suffer from insufficient and uncontrollable mechanical and degradation properties. In
Jason W Nichol et al.
Biomaterials, 31(21), 5536-5544 (2010-04-27)
The cellular microenvironment plays an integral role in improving the function of microengineered tissues. Control of the microarchitecture in engineered tissues can be achieved through photopatterning of cell-laden hydrogels. However, despite high pattern fidelity of photopolymerizable hydrogels, many such materials
Anh H Nguyen et al.
Acta biomaterialia, 13, 101-110 (2014-12-03)
Gelatin has been commonly used as a delivery vehicle for various biomolecules for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications due to its simple fabrication methods, inherent electrostatic binding properties, and proteolytic degradability. Compared to traditional chemical cross-linking methods, such as
Chaenyung Cha et al.
Biomacromolecules, 15(1), 283-290 (2013-12-19)
Microfabrication technology provides a highly versatile platform for engineering hydrogels used in biomedical applications with high-resolution control and injectability. Herein, we present a strategy of microfluidics-assisted fabrication photo-cross-linkable gelatin microgels, coupled with providing protective silica hydrogel layer on the microgel
Luiz E Bertassoni et al.
Biofabrication, 6(2), 024105-024105 (2014-04-04)
Fabrication of three dimensional (3D) organoids with controlled microarchitectures has been shown to enhance tissue functionality. Bioprinting can be used to precisely position cells and cell-laden materials to generate controlled tissue architecture. Therefore, it represents an exciting alternative for organ
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.