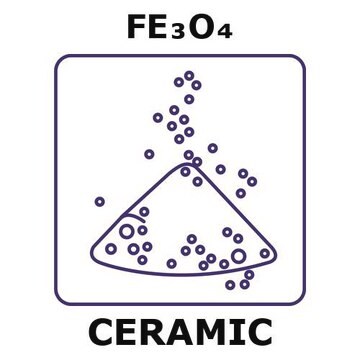
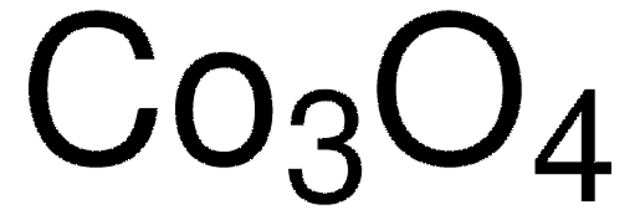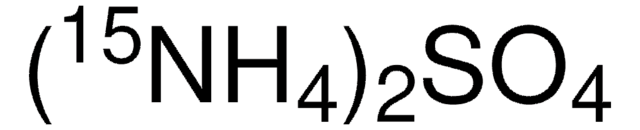추천 제품
설명
crystalline (primarily γ)
Quality Level
양식
nanopowder
표면적
50-245 m2/g
입자 크기
<50 nm (BET)
응용 분야
battery manufacturing
SMILES string
O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O
InChI
1S/2Fe.3O
InChI key
JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
일반 설명
애플리케이션
특징 및 장점
- High theoretical specific capacity
- Biocompatibility
- Ease of coating and modification
- Non-toxicity
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
이미 열람한 고객
문서
Innovation in dental restorative materials is driven by the need for biocompatible and natural-appearing restoration alternatives. Conventional dental materials like amalgam and composite resins have inherent disadvantages.
Currently, magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are attracting a lot of attention because of the possibility of many novel applications, especially in biomedical research.
Graphene is a unique two-dimensional (2D) structure of monolayer carbon atoms packed into a dense honeycomb crystal that has attracted great interest due to its diverse and fascinating properties.
Professor Hui Mao explores the use of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (INOPs) that offer an alternate contrast-enhancing mechanism.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 544884-25G | 4061838254061 |
| 544884-5G | 4061832567815 |
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.