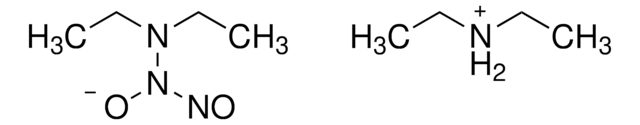M5793
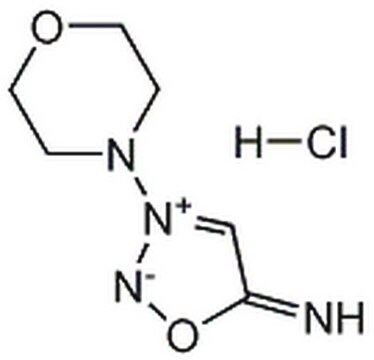
3-Morpholinosydnonimine hydrochloride
(consistent with structure, NMR)
Synonym(s):
3-(4-Morpholinyl)sydnone imine hydrochloride, Linsidomine hydrochloride, SIN-1 hydrochloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C6H10N4O2 · HCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
206.63
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl[H].[NH-]c1c[n+](no1)N2CCOCC2
InChI
1S/C6H10N4O2.ClH/c7-6-5-10(8-12-6)9-1-3-11-4-2-9;/h5,7H,1-4H2;1H
InChI key
NCGICGYLBXGBGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
3-Morpholinosydnonimine hydrochloride has been used:
- as a peroxynitrite donor standard to study the accumulation of peroxynitrite in Arabidopsis thaliana
- to study its effects on nitrosative stress in human brain vascular pericytes and human embryonic kidney cells
- as a ROS to study its effects on mouse embryonic fibroblasts
Biochem/physiol Actions
3-Morpholinosydnonimine participates in the inhibition of cysteine proteases.
Liberates nitric oxide (NO) spontaneously when in solution, activating guanylyl cyclase and causing an increase in cyclic-GMP. This product is a vasodilator and inhibits platelet aggregation. Using molecular oxygen, it generates both superoxide anion and nitric oxide that spontaneously form peroxynitrite.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Frank Gaupels et al.
Nitric oxide : biology and chemistry, 25(2), 222-228 (2011-02-08)
Nitric oxide (NO) is synthesized in plants in response to stress, and its role in signaling is well-documented. In contrast, very little is known about the physiological role of its derivate peroxynitrite (ONOO(-)), which forms when NO reacts with O(2)(-)
Keren Zohar et al.
Biomedicines, 9(9) (2021-09-29)
A hallmark of the aging brain is the robust inflammation mediated by microglial activation. Pathophysiology of common neurodegenerative diseases involves oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Chronic treatment of aging rats by ladostigil, a compound with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory function, prevented microglial
H de Groot et al.
FEBS letters, 315(2), 139-142 (1993-01-04)
SIN-1 which spontaneously decomposes to yield nitric oxide (NO.) and superoxide anion (O2.-) radicals caused a loss of microsomal alpha-tocopherol paralleled by the formation of alpha-tocopheryl quinone. The loss was partially prevented by superoxide dismutase but not by catalase. The
Kittipot Sirichaiwetchakoon et al.
BioMed research international, 2020, 4183643-4183643 (2020-10-09)
Tea is one of the most popular beverages in the world. Camellia sinensis tea (CST) or green tea is widely regarded as a potent antioxidant. In Thailand, Pluchea indica (L.) Less. tea (PIT) has been commercially available as a health-promoting
Mushfiquddin Khan et al.
Journal of neuroinflammation, 8, 78-78 (2011-07-08)
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) induces primary and secondary damage in both the endothelium and the brain parenchyma, collectively termed the neurovascular unit. While neurons die quickly by necrosis, a vicious cycle of secondary injury in endothelial cells exacerbates the initial
Related Content
DISCOVER Bioactive Small Molecules for Nitric Oxide & Cell Stress Research
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service