D5439
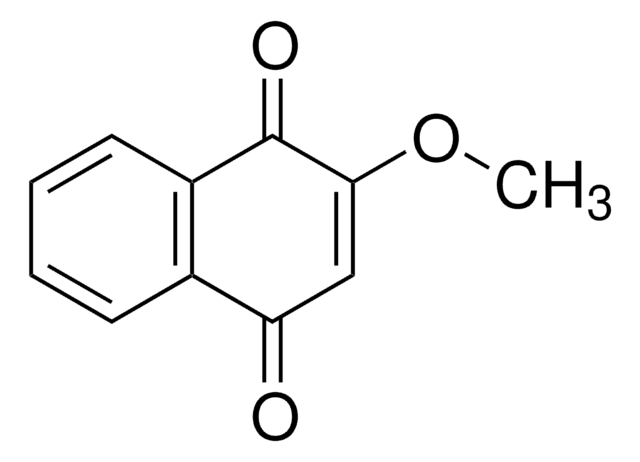
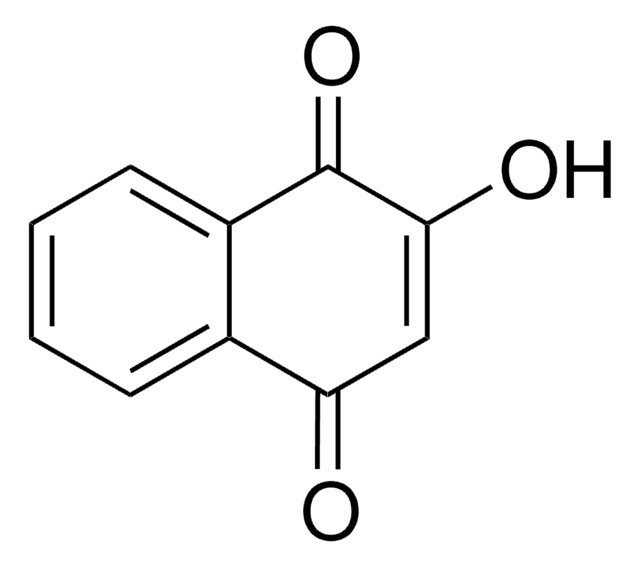
2,3-Dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone
≥99%, solid
Synonym(s):
DMNQ
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C12H10O4
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
218.21
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥99%
form
solid
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
COC1=C(OC)C(=O)c2ccccc2C1=O
InChI
1S/C12H10O4/c1-15-11-9(13)7-5-3-4-6-8(7)10(14)12(11)16-2/h3-6H,1-2H3
InChI key
ZEGDFCCYTFPECB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
2,3-Dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone has been used to investigate the effects of ethanol on podocyte apoptosis under hypoxic and hyperoxic conditions.
Used to study the role of ROS in cell toxicity, apoptosis, and necrosis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
2,3-dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (DMNQ) has the ability to produce H2O2 through redox cycling but fails to conjugate with glutathione (GSH).
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Acute ethanol induces apoptosis by stimulating TRPC6 via elevation of superoxide in oxygenated podocytes
Lu X Y, et al.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Molecular Cell Research, 1853(5), 965-974 (2015)
Anne R Diers et al.
Redox biology, 1, 1-7 (2013-09-12)
Nitric oxide production by the endothelium is required for normal vascular homeostasis; however, in conditions of oxidative stress, interactions of nitric oxide with reactive oxygen species (ROS) are thought to underlie endothelial dysfunction. Beyond canonical nitric oxide signaling pathways, nitric
Tindaro M Giardina et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1777(2), 118-129 (2007-12-18)
Uncoupling protein-2 (UCP2) is a member of the inner mitochondrial membrane anion-carrier superfamily. Although mRNA for UCP2 is widely expressed, protein expression is detected in only a few cell types, including macrophages. UCP2 functions by an incompletely defined mechanism, to
Richard Eugene Frye et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 4478-4478 (2017-07-02)
Mitoplasticity occurs when mitochondria adapt to tolerate stressors. Previously we hypothesized that a subset of lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) from children with autistic disorder (AD) show mitoplasticity (AD-A), presumably due to previous environmental exposures; another subset of AD LCLs demonstrated
Valerie P Wright et al.
The Journal of physiology, 587(Pt 23), 5767-5781 (2009-10-21)
Skeletal muscles produce transient reactive oxygen species (ROS) in response to intense stimulation, disuse atrophy, heat stress, hypoxia, osmotic stress, stretch and cell receptor activation. The physiological significance is not well understood. Protein phosphatases (PPases) are known to be highly
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service