690708
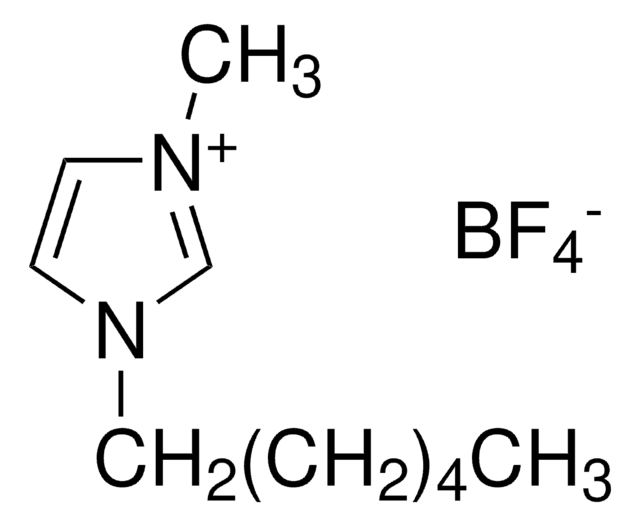
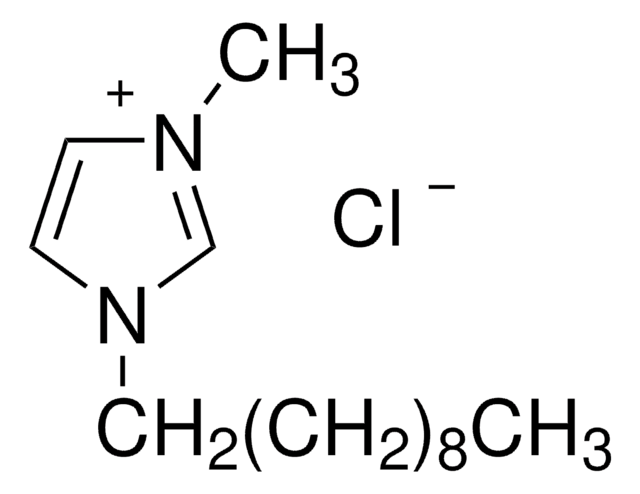
1-Decyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate
≥96.5% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
[C10MIM][BF4]
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C14H27BF4N2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
310.18
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥96.5% (HPLC)
form
liquid
impurities
≤0.3% water
refractive index
n20/D 1.438-1.450
SMILES string
F[B-](F)(F)F.CCCCCCCCCCn1cc[n+](C)c1
InChI
1S/C14H27N2.BF4/c1-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-16-13-12-15(2)14-16;2-1(3,4)5/h12-14H,3-11H2,1-2H3;/q+1;-1
InChI key
QGUMDWFYJYXDTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
1-Decyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate is an ionic liquid, which can be used as:
- A clathrate hydrate crystal inhibitor in drilling fluid.
- A microextraction solvent in the determination of synthetic dyes in foods and cosmetics.
- A substrate in the host-guest inclusion complexation studies with β-cyclodextrin.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Inclusion complexation of imidazolium-based ionic liquid and beta-cyclodextrin: A detailed spectroscopic investigation
Banjare MK, et al.
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 302, 112530-112530 (2020)
Determination of Brilliant Blue FCF in food and cosmetic samples by ionic liquid independent disperse liquid--liquid micro-extraction
Guo J, et al.
Analytical Methods : Advancing Methods and Applications, 5(16), 4021-4026 (2013)
Evaluation of 1-Decyl-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate as clathrate hydrate crystal inhibitor in drilling fluid
Saikia T and Mahto V
Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 36, 906-915 (2016)
S Mitra et al.
European biophysics journal : EBJ, 48(2), 119-129 (2018-11-27)
The large number of potential applications of ionic liquids (ILs) requires an understanding of their environmental impacts including their adverse effects on microorganisms living in soil and water. The molecular mechanism of toxic activities of these liquids is yet to
Saheli Mitra et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta. Biomembranes, 1863(6), 183589-183589 (2021-03-03)
Ionic liquids (ILs) are the attractions of researchers today due to their vast area of potential applications. For biomedical uses, it becomes essential to understand their interactions with cellular membrane. Here, the membrane is mimicked with lipid bilayer and monolayer
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service