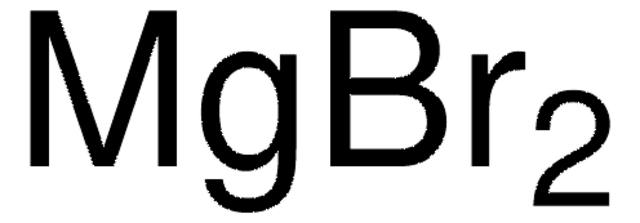449164
Magnesium chloride
AnhydroBeads™, −10 mesh, 99.9% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Magnogene
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
MgCl2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
95.21
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352302
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
product line
AnhydroBeads™
Quality Level
Assay
99.9% trace metals basis
impurities
≤1500.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
refractive index
n20/D 1.675 (lit.)
particle size
−10 mesh
mp
714 °C (lit.)
solubility
H2O: slightly soluble(lit.)
density
2.32 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
Cl[Mg]Cl
InChI
1S/2ClH.Mg/h2*1H;/q;;+2/p-2
InChI key
TWRXJAOTZQYOKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) is an inorganic compound that can be prepared by reacting magnesium oxide and ammonium chloride in the presence of alumina as a covering agent.
Application
MgCl2 can be used in a variety of applications such as a precursor to magnesium metal, catalyst support in Ziegler-Natta catalyst and in food processing.
Legal Information
AnhydroBeads is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
accessory
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Magnesium compounds
Seeger M, et al.
Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 101(12), 4646-4655 (2000)
Preparation of anhydrous magnesium chloride from magnesia
Zhang Z, et al.
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 51(29), 9713-9718 (2012)
Commercially available metal alkyls and their use in polyolefin catalysts
Handbook of Transition Metal Polymerization Catalysts, 101(12), 1-28 (2010)
Pushkaraj R Patwardhan et al.
Bioresource technology, 101(12), 4646-4655 (2010-02-23)
Processing bio-oil with the help of currently existing petroleum refinery infrastructure has been considered as a promising alternative to produce sustainable fuels in the future. The feasibility of bio-oil production and upgrading processes depend upon its chemical composition which in
Bert De Rybel et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 345(6197), 1255215-1255215 (2014-08-12)
Coordination of cell division and pattern formation is central to tissue and organ development, particularly in plants where walls prevent cell migration. Auxin and cytokinin are both critical for division and patterning, but it is unknown how these hormones converge
Protocols
Summary application report for analysis of moisture in Magnesium chloride
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service