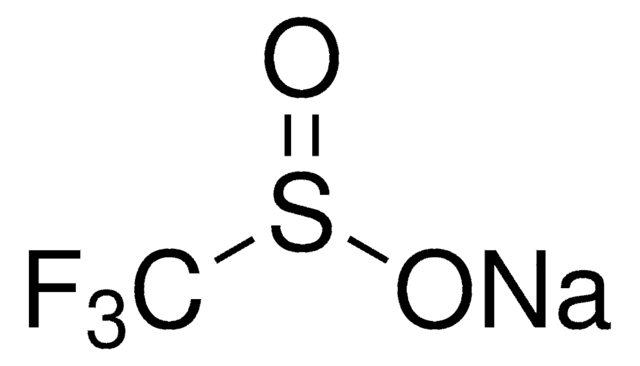
433063
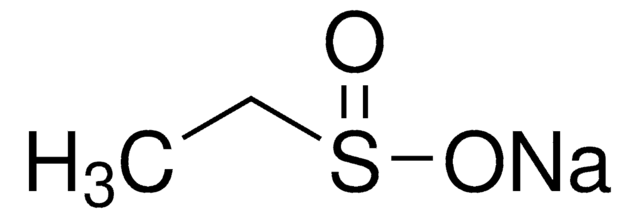
Sodium methanesulfinate
technical grade, 85%
Synonym(s):
Methanesulfinic acid sodium salt
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CH3SO2Na
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
102.09
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
grade
technical grade
Quality Level
Assay
85%
mp
222-226 °C (dec.) (lit.)
functional group
sulfinic acid
SMILES string
[Na+].CS([O-])=O
InChI
1S/CH4O2S.Na/c1-4(2)3;/h1H3,(H,2,3);/q;+1/p-1
InChI key
LYPGDCWPTHTUDO-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Sodium methanesulfinate is an aliphatic sodium sulfinate. Conjugate addition of sodium methanesulfinate to vinyl heterocycles has been described. Cross-coupling reaction between aryl boronic acid and sodium methanesulfinate has been studied. Its stock solution was prepared from methanesulfonic acid by adding one equivalent of sodium hydroxide and diluting it to 4M.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Metal-Free Direct Construction of Sulfonamides via Iodine-Mediated Coupling Reaction of Sodium Sulfinates and Amines at Room Temperature.
Wei W, et al.
Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 357(5), 987-992 (2015)
J B Smith et al.
Free radical research communications, 8(2), 101-106 (1990-01-01)
Iron bound to certain chelators is known to promote the conversion of superoxide radicals (O2-) to hydroxyl radicals (HO.) by the superoxide-driven Fenton reaction. The production of HO. by various iron chelates was studied using the reaction of dimethyl sulfoxide
M G Steiner et al.
Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 278(2), 478-481 (1990-05-01)
This investigation was conducted to validate the use of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as a quantitative molecular probe for the generation of hydroxyl radicals (HO.) in aqueous systems. Reaction of HO. with DMSO produces methane sulfinic acid as a primary product
M G Steiner et al.
Free radical biology & medicine, 9(1), 67-77 (1990-01-01)
To quantitate the formation of hydroxyl radicals (HO.) in ischemia and reoxygenation, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was added to "trap" evolving HO. in normal, in ischemic, and in ischemic and reoxygenated rat kidney slices, incubated in short-term organ culture in vitro.
S Fukui et al.
Journal of chromatography, 630(1-2), 187-193 (1993-02-05)
For the determination of hydroxyl radicals, dimethyl sulphoxide was used as a molecular probe and the methanesulphinic acid produced was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography of its Fast Yellow GC salt derivative. The results for hydroxyl radicals formed using the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service

![1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/120/564/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb/640/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb.png)