167703
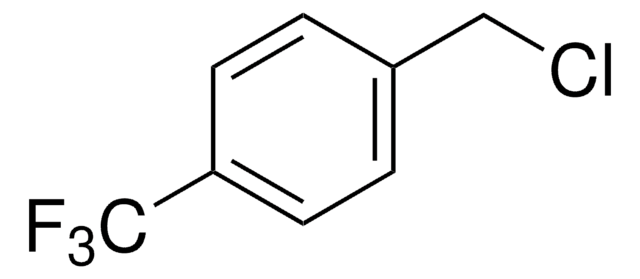
3-(Trifluoromethyl)benzyl chloride
97%
Synonym(s):
α′-Chloro-α,α,α-trifluoro-m-xylene, 3-(Chloromethyl)benzotrifluoride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CF3C6H4CH2Cl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
194.58
Beilstein:
743242
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
97%
form
liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.464 (lit.)
density
1.254 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
functional group
chloro
fluoro
SMILES string
FC(F)(F)c1cccc(CCl)c1
InChI
1S/C8H6ClF3/c9-5-6-2-1-3-7(4-6)8(10,11)12/h1-4H,5H2
InChI key
XGASTRVQNVVYIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
3-(Trifluoromethyl)benzyl chloride reacts with sodium salts of N,N-disubstituted dithiocarbamic acids to yield series of dithiocarbamates.
Application
3-(Trifluoromethyl)benzyl chloride was used in the synthesis of 4-nitro-3-trifluoromethyl-[N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)]benzamide.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
118.4 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
48 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Synthesis of poly (arylene ether amide) s containing CF 3 groups by nitro displacement reaction of AB-type monomers.
Lee HS and Kim SY.
Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 23(12), 665-671 (2002)
Mehlika D Altıntop et al.
Archiv der Pharmazie, 346(8), 571-576 (2013-07-25)
In the present paper, a novel series of dithiocarbamates was synthesized via the treatment of 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl chloride with appropriate sodium salts of N,N-disubstituted dithiocarbamic acids. The chemical structures of the compounds were elucidated by (1) H NMR, mass spectral data
William L Scott et al.
Journal of combinatorial chemistry, 11(1), 14-33 (2008-12-25)
Distributed Drug Discovery (D(3)) proposes solving large drug discovery problems by breaking them into smaller units for processing at multiple sites. A key component of the synthetic and computational stages of D(3) is the global rehearsal of prospective reagents and
William L Scott et al.
Journal of combinatorial chemistry, 11(1), 34-43 (2008-12-25)
For the successful implementation of Distributed Drug Discovery (D(3)) (outlined in the accompanying Perspective), students, in the course of their educational laboratories, must be able to reproducibly make new, high quality, molecules with potential for biological activity. This article reports
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service