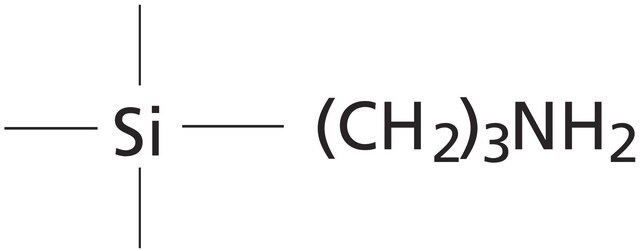52636-U
Discovery® DSC-NH2 SPE Tube
bed wt. 100 mg, volume 1 mL, pk of 108
Synonym(s):
NH2 (amine) SPE cartridge tube
About This Item
Recommended Products
material
PE frit (20 μm)
polypropylene
feature
endcapped
composition
bed wt., 100 mg
packaging
pk of 108
technique(s)
solid phase extraction (SPE): suitable
surface area
480 m2/g
volume
1 mL
matrix
silica gel base material (irregularly shaped, acid washed)
matrix active group
amino phase
particle size
50 μm
pore size
70 Å pore size
pKa
9.8
capacity
~0.43 meq/g capacity
application(s)
food and beverages
separation technique
ion exchange
normal phase
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Sample Matrix Compatibility: Organic or aqueous solutions
- Polymerically bonded, aminopropyl phase that is very polar in nature (hydrogen bonding) allowing for both normal phase and ion exchange applications
- A weak anion exchanger with a pKa of 9.8. At pH 7.8 or below, the functional groups are positively charged
- Ion exchange capacity is ∼ 0.43 meq/g.
- Allows the rapid release of very strong anions such as sulfonic acids that may be retained irreversibly by strong anion exchangers
- Can be used in some reversed-phase applications (due to ethyl spacer); however, it is predominately used as an ion-exchange or normal phase sorbent due to its polar nature
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
>464.0 °F
Flash Point(C)
> 240 °C
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
52636-U:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
SPE retention mechanism in this case is based on the electrostatic attraction of charged functional groups of the analyte(s) to oppositely charged functional groups on the sorbent.
Protocols
Retention occurs through polar interaction between the sorbent and analytes. Typical sample matrices that can be employed in normal-phase SPE include hydrocarbon or fatty oils diluted in a solvent like hexane, isooctane, chlorinated solvent, THF, diethyl ether, or ethyl acetate.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service