P9386
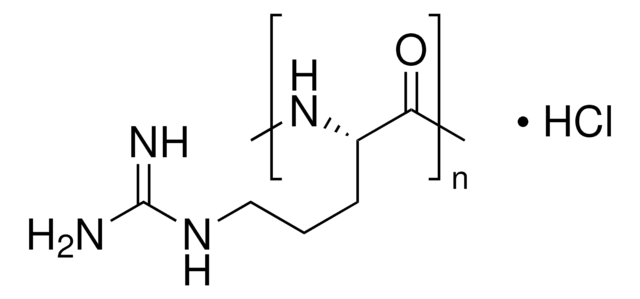
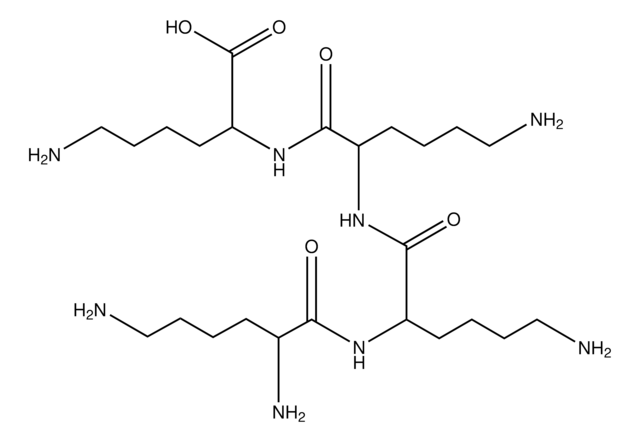
Poly-L-histidine
mol wt 5,000-25,000
Synonym(s):
L-Histidine homopolymer
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
powder or solid
Quality Level
mol wt
5,000-25,000
color
white to light yellow
application(s)
cell analysis
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
1S/C6H9N3O2/c7-5(6(10)11)1-4-2-8-3-9-4/h2-3,5H,1,7H2,(H,8,9)(H,10,11)/t5-/m0/s1
InChI key
HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-YFKPBYRVSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- as a polycation for the dispersion of multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)
- as a polyionic compound to investigate its ability to rupture extracellular enveloped virus membrane
- in screening its anti-prion activity in cell based and in vivo anti-prion assay
Biochem/physiol Actions
Analysis Note
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
P9386-50MG:
P9386-VAR:
P9386-100MG:
P9386-10MG:
P9386-BULK:
P9386-2MG:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Humankind has utilized protein materials throughout its existence, starting with the use of materials such as wool and silk for warmth and protection from the elements and continuing with the use of recombinant DNA techniques to synthesize proteins with unique and useful properties.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service