FLAA
Adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) Bioluminescent Assay Kit
for ATP quantitation
Synonym(s):
ATP Bioluminescence Assay, ATP Determination Kit, Luminescent ATP Detection kit
About This Item
Recommended Products
storage temp.
−20°C
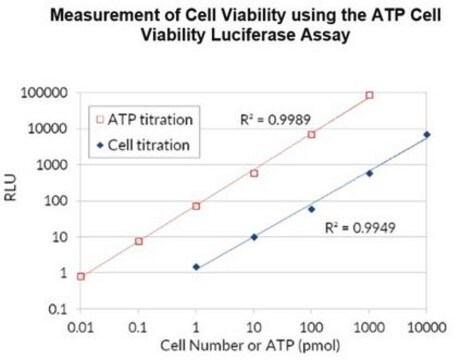
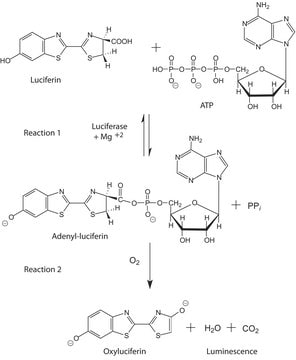
General description
Application
Kit Components Only
- FL-AAB Dilution buffer 1 mL/vial
- FL-AAM Assay mix 1 mL/vial
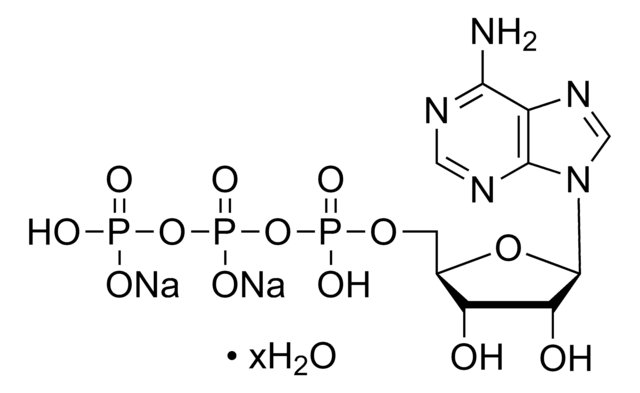
- FL-AAS ATP standard 1 mL/vial
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
PDSCL
Please refer to KIT Component information
PRTR
Please refer to KIT Component information
FSL
Please refer to KIT Component information
ISHL Indicated Name
Please refer to KIT Component information
ISHL Notified Names
Please refer to KIT Component information
Cartagena Act
Please refer to KIT Component information
JAN Code
キットコンポーネントの情報を参照してください
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service