C6137
Chitinase from Streptomyces griseus
lyophilized powder (essentially salt free), ≥200 units/g solid
Synonym(s):
N-acetyl-glucosaminidasechitobiase, Chitin digestion enzymes, poly(β-(1→4)-[2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucoside])- glycanohydrolase
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
lyophilized powder (essentially salt free)
Quality Level
specific activity
≥200 units/g solid
mol wt
30 kDa
solubility
H2O: soluble 0.90-1.10 mg/mL
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
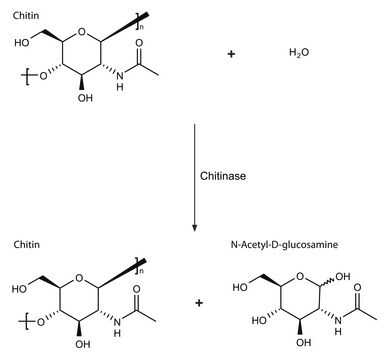
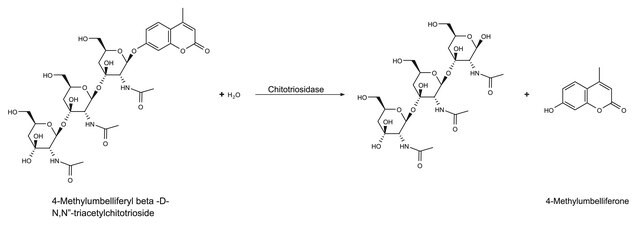
The enzymatic hydrolysis of chitin to N-acetyl-D-glucosamine involves two consecutive enzyme reactions:
- The first reaction, chitodextrinase-chitinase, is a poly(β-(1→4)-[2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucoside])- glycanohydrolase, which removes chitobiose units from chitin.
- The second activity is N-acetyl-glucosaminidasechitobiase, which cleaves the disaccharide to its monomer subunits, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine.
Application
Human health care: Asthma.
Pharma: preparation of chitooligosaccharides and N-acetyl D glucosamine,
Preparation of single-cell protein
Isolation of protoplasts from fungi and yeast
Control of pathogenic fungi
Treatment of chitinous waste, mosquito control and morphogenesis
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Unit Definition
One new 1 hour unit = approx. 50 old 48 hour units.
substrate
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
C6137-5UN-PW:
C6137-25UN-PW:
C6137-50UN-PW:
C6137-5UN:
C6137-VAR:
C6137-RSAMPLE:
C6137-50UN:
C6137-25UN:
C6137-2.5UN:
C6137-BULK:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Related Content
Protein extraction kits, cell lysis buffers, and reagents for solubilizing proteins from bacteria, yeast, and insect cultures, as well as plant and mammalian cell cultures and tissue samples.
An overview of cell lysis and protein extraction methods including detergent solubilization, freeze-thaw lysis, osmotic shock, sonication, enzymatic cell lysis, and mechanical disruption techniques such as Dounce, Polytron, and mortar and pestle homogenization.
An overview of cell lysis and protein extraction methods including detergent solubilization, freeze-thaw lysis, osmotic shock, sonication, enzymatic cell lysis, and mechanical disruption techniques such as Dounce, Polytron, and mortar and pestle homogenization.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service