C1386
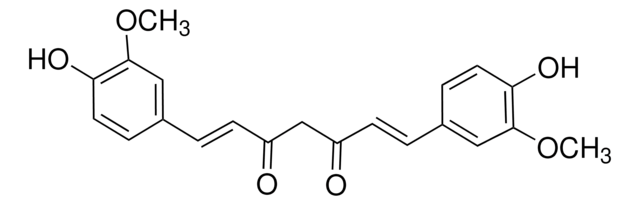
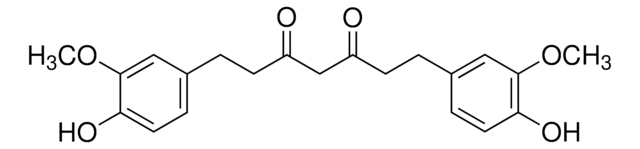
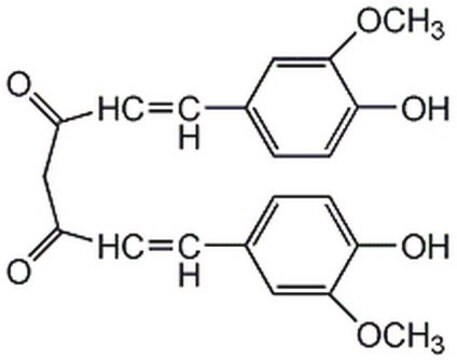
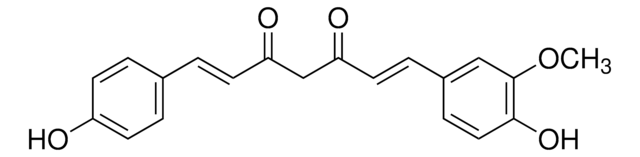
Curcumin
from Curcuma longa (Turmeric), powder
Synonym(s):
(E,E)-1,7-bis(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione, Diferuloylmethane, Diferulylmethane, Natural Yellow 3
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Curcuma longa (Turmeric)
Quality Level
vapor density
13 (vs air)
form
powder
concentration
≥65% (HPLC)
mp
175 °C
solubility
ethanol: 10 mg/mL
DMSO: >11 mg/mL (lit.)(lit.)
0.5 M NaOH: soluble (then immediately dilute in PBS [lit.])(lit.)
application(s)
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
COc1cc(\C=C\C(=O)CC(=O)\C=C\c2ccc(O)c(OC)c2)ccc1O
InChI
1S/C21H20O6/c1-26-20-11-14(5-9-18(20)24)3-7-16(22)13-17(23)8-4-15-6-10-19(25)21(12-15)27-2/h3-12,24-25H,13H2,1-2H3/b7-3+,8-4+
InChI key
VFLDPWHFBUODDF-FCXRPNKRSA-N
Gene Information
human ... APP(351) , CYP1A2(1544)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- to study its effect on the consequences and mechanism involved in the suppression of human homeobox gene NKX3.1 in the prostate cancer cell LNCaP
- to examine its effect on stress in pigs by having an inhibitory impact on the serum cortisol concentration, hippocampal nitric oxide production, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression
- to study its effect as a dietary supplement on the growth, immunity, antioxidant activity, and disease resistance in Oreochromis niloticus
- to analyze its protective effect on the organotypic hippocampal slice cultures against the synaptic toxicity caused by amyloid beta peptides (Aβ1–42)
- to examine the possibility of its non-toxic concentrations to decrease the inflammation caused by interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) in cartilage explant cultures
- to study its protective impact against intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats
- to measure its antibacterial activity in vitro
- to determine its preventative effects for Alzheimer′s disease (AD) in mice
- as a bifunctional agent for generation and validation of the erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) reporter system
- to study its in vitro inhibitory effects on human liver glucuronidation activity
- to evaluate its effects on Parkinson′s disease (PD)-like phenotypes
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
C1386-BULK:
C1386-50G:
C1386-10G:
C1386-5G:
C1386-VAR:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Epigenetic modifications are thought to occur through two key interconnected processes—DNA methylation and the covalent modification of histones.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service