37272
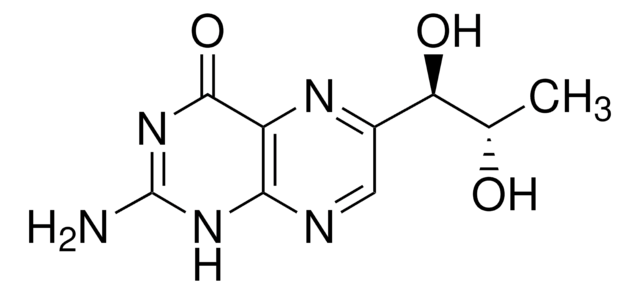
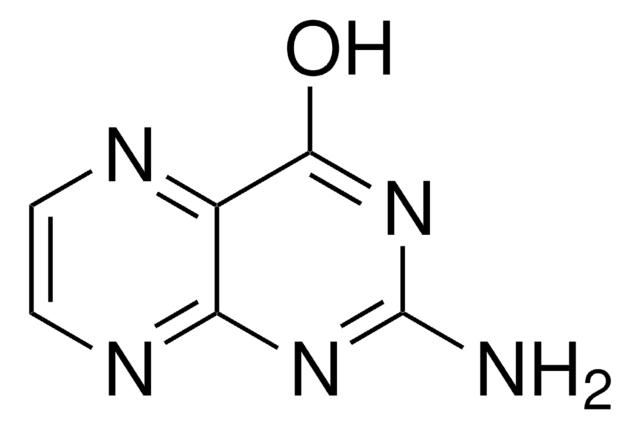
7,8-Dihydro-L-biopterin
≥94% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
2-amino-6-(1,2-dihydroxypropyl)-7,8-dihydro-3H-pteridin-4-one
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥94% (HPLC)
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
C[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C1=NC2=C(NC1)N=C(N)NC2=O
InChI
1S/C9H13N5O3/c1-3(15)6(16)4-2-11-7-5(12-4)8(17)14-9(10)13-7/h3,6,15-16H,2H2,1H3,(H4,10,11,13,14,17)/t3-,6-/m1/s1
InChI key
FEMXZDUTFRTWPE-AWFVSMACSA-N
Application
- A Landscape of Metabonomics for Intermingled Phlegm and Blood Stasis and Its Concurrent Syndromes in Stable Angina Pectoris of Coronary Heart Disease.: This study by Zheng et al. (2022) explores the metabolic profiles associated with phlegm and blood stasis syndromes in patients with stable angina pectoris. The research highlights the role of various metabolites, including 7,8-Dihydro-ʟ-biopterin, in the pathophysiology of these syndromes, suggesting potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets (Zheng et al., 2022).
- Three-dimensional structure of human tryptophan hydroxylase and its implications for the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin and melatonin.: Wang et al. (2002) present the crystal structure of human tryptophan hydroxylase, providing detailed insights into the enzyme′s interaction with cofactors such as 7,8-Dihydro-ʟ-biopterin. This structural information is crucial for developing drugs targeting neurotransmitter biosynthesis pathways (Wang et al., 2002).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
37272-VAR:
37272-BULK:
37272-10MG:
37272-50MG:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service