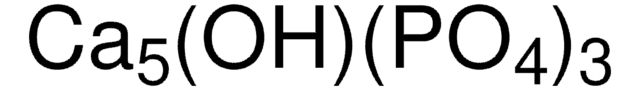49963
β-tri-Calcium phosphate
puriss. p.a., ≥98% β-phase basis (sintered Powder)
Synonym(s):
β-TCP, β-Tricalcium phosphate
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
puriss. p.a.
Quality Level
Assay
≥98% β-phase basis (sintered Powder)
form
powder
impurities
≤50 mg/kg total heavy metals as lead
≤500 mg/kg total sulfur as SO4 (ICP)
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 mg/kg
cation traces
As: ≤0.5 mg/kg
Ba: ≤20 mg/kg
Cd: ≤1 mg/kg
Co: ≤1 mg/kg
Cr: ≤10 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Hg: ≤0.5 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤20 mg/kg
InChI
1S/3Ca.2H3O4P/c;;;2*1-5(2,3)4/h;;;2*(H3,1,2,3,4)/q3*+2;;/p-6
InChI key
QORWJWZARLRLPR-UHFFFAOYSA-H
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
- Tungstosilicic Acid: A Promising Electrolyte for Redox Flow Battery.: This study explores the use of tungstosilicic acid (TSA) as an electrolyte in redox flow batteries (RFB). The research highlights TSA′s high energy density due to its multi-electron transfer capability, making it a promising candidate for enhancing the efficiency and power density of RFBs. This advancement is particularly relevant for large-scale energy storage systems integrating renewable energy technologies (Sharma et al., 2023).
- Heterogenization of a Tungstosilicic Acid Catalyst for Esterification of Bio-Oil Model Compound.: This paper explores the heterogenization of tungstosilicic acid by supporting it on silica-based materials for the esterification of bio-oil model compounds. The catalyst shows high activity and stability, indicating its potential for industrial applications in bio-oil upgrading (Prasertpong et al., 2022).
Analysis Note
ß-TCP: >98% ; Hydroxylapatite: <1.0% ; a-TCP: <0%; TTCP: 0%
other Ca-P phases as Calcium pyrophosphate <1.0%
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
49963-VAR:
49963-BULK:
49963-100G:
49963-10G:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service