79266
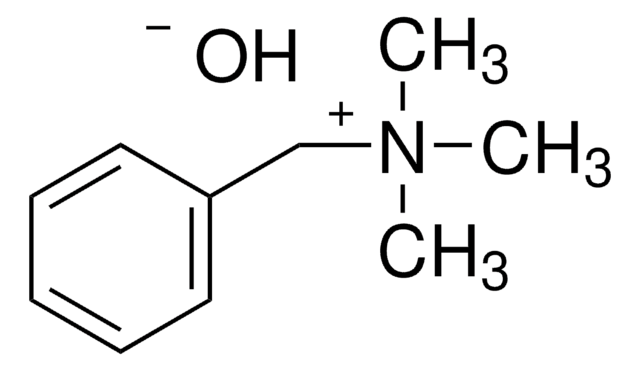
Trimethylphenylammonium hydroxide solution
~0.5 M (CH3)3N(OH)C6H5 in methanol, for GC derivatization, LiChropur™
Synonym(s):
Phenyltrimethylammonium hydroxide, TMAH
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
derivatization grade ((GC derivatization))
for GC derivatization
Quality Level
form
liquid
quality
LiChropur™
reaction suitability
reagent type: derivatization reagent
reaction type: Esterifications
concentration
~0.5 M (CH3)3N(OH)C6H5 in methanol
technique(s)
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
impurities
≤0.2% halides (as chloride)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[OH-].C[N+](C)(C)c1ccccc1
InChI
1S/C9H14N.H2O/c1-10(2,3)9-7-5-4-6-8-9;/h4-8H,1-3H3;1H2/q+1;/p-1
InChI key
HADKRTWCOYPCPH-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Other Notes
Legal Information
Disclaimer
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Corr. 1B - STOT SE 1
Target Organs
Eyes
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
51.8 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
11 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
FSL
Group 4: Flammable liquids
Alcohols
Hazardous rank II
ISHL Indicated Name
Substances Subject to be Indicated Names
ISHL Notified Names
Substances Subject to be Notified Names
JAN Code
79266-1ML-KC:
79266-10ML:4548173179971
79266-10X1ML:4548173908052
79266-BULK:
79266-VAR:
79266-50ML:4548173179988
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service