69732
Lithium mupirocin Supplement
suitable for microbiology, Selectively inhibits the growth of lactic acid bacteria
Synonym(s):
Lithium mupirocin solution, Li-MUP, MUP supplement
About This Item
Recommended Products
Agency
ISO 29981:2010
Quality Level
sterility
sterile (Filtered and Aseptic Handled)
sterile
form
liquid
shelf life
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
application(s)
environmental
food and beverages
microbiology
storage temp.
2-8°C
suitability
Lactobacillus spp.
Lactococcus spp.
Leuconostoc spp.
Streptococcus spp.
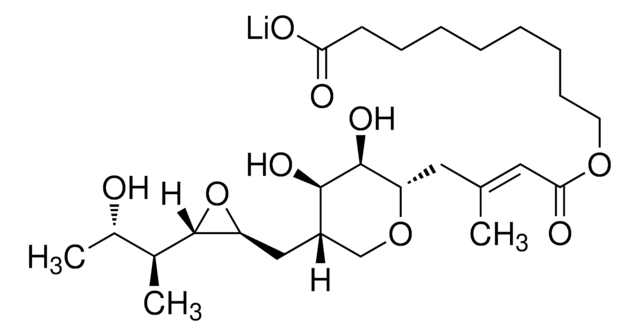
SMILES string
[Li+].C[C@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@@H]1O[C@H]1C[C@H]2CO[C@@H](C\C(C)=C\C(=O)OCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]2O
InChI
1S/C26H44O9.Li/c1-16(13-23(30)33-11-9-7-5-4-6-8-10-22(28)29)12-20-25(32)24(31)19(15-34-20)14-21-26(35-21)17(2)18(3)27;/h13,17-21,24-27,31-32H,4-12,14-15H2,1-3H3,(H,28,29);/q;+1/p-1/b16-13+;/t17-,18-,19-,20-,21-,24+,25-,26-;/m0./s1
InChI key
XFIKMPRBSORKQP-JATHGWPISA-M
General description
Application
Components
(5ml, sufficient for 100 ml medium)
Mupirocin 5 mg
sterile distilled water 5.0 ml
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
69732-VAR:
69732-10X25ML:
69732-BULK:
69732-25ML:
69732-10X5ML:
69732-5ML:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service