General description
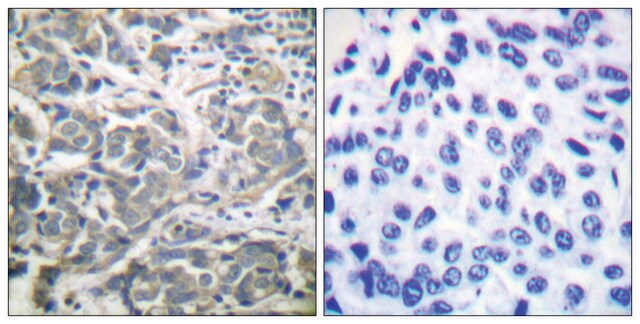
SCC625, the mEERL Lung Metastasis cell line (MLM), is one of the clones isolated from the lung metastasis of the inoculation of SCC627 mEERL cells that formed after the apparent disease clearance following a treatment by cisplatin and radiation. SCC625 was shown to be inherently more resistant to treatment than its parent. SCC625 showed ready tropism to the lungs upon re-injection into immunocompetent mice, plus a higher rate of metastasis and a greater number of metastatic tumors than its parent or the four other sibling clones isolated in parallel. While this clone has lost the luciferase expression of the parental SCC627, it retains the expression of many of the hallmark genes of OPSCC, including cytokeratin, E-cadherin, BRCA2, p16, and EGFR, and its spread has been tracked in vivo by such markers.
Application
MLM cells are verified to be of mouse origin and negative for human, rat, Chinese hamster, Golden Syrian hamster, and non-human primate interspecies contamination, as assessed by a Contamination Clear panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic ServicesCells tested negative for infectious diseases against a Mouse Essential CLEAR panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services.Cells tested negative for mycoplasma.
Features and Benefits
SCC625 MLM.3 Mouse Lung Metastasis Cell Line is a recurrent/metastatic model of HPV+ (human papilloma virus-positive) OPSCC cancers, and retains the heterogeneity and resistance characteristics of refractory human disease to serve as a translational system to test novel therapeutics.
Target description
Head and neck cancers represent the sixth most common cancers worldwide. Among them, incidence of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) are increasing, and a majority are caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV). While successful management methods exist, local recurrence and nodal metastasis result in mortality in a minority of cases. Historically, insights into HPV-induced transformation have been obtained in the context of cervical cancer and anogenital warts models. While much of this is relevant to OPSCC, systems in which the effects of HPV infection can be studied in the context specific to OPSCC are critical.SOURCESCC625 cell line is a clone isolated from the lung metastasis of the mEERL cell line (SCC627) in a treatment-failed male C57BL/6 mouse. SCC627 is a luciferase-expressing derivative of the mEER cell line (SCC626). SCC626 was established by the retroviral transduction of the HPV16 E6 gene, HPV16 E7 gene, and the human hRas gene into the primary oropharyngeal epithelial cells isolated from a male C57BL/6 mouse.REFERENCES1.Kademani D. 2007. Oral cancer. Mayo Clin Proc. 82(7): 878-87. 2.Rogers SN, Brown JS, Woolgar JA, Lowe D, Magennis P, Shaw RJ, Sutton D, Errington D, Vaughan D. 2009. Survival following primary surgery for oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 45(3):201-11. 3.Pytynia KB, Dahlstrom KR, Sturgis EM. 2014. Epidemiology of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 50(5): 380-6. 4.Hoover AC, Spanos WC, Harris GF, Anderson ME, Klingelhutz AJ, Lee JH. 2007. The role of human papillomavirus 16 E6 in anchorage-independent and invasive growth of mouse tonsil epithelium. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 133(5): 495-502. 5.Williams R, Lee DW, Elzey BD, Anderson ME, Hostager BS, Lee JH. 2009. Preclinical models of HPV+ and HPV- HNSCC in mice: an immune clearance of HPV+ HNSCC. Head Neck. 31(7): 911-8. 6.Vermeer DW, Coppock JD, Zeng E, Lee KM, Spanos WC, Onken MD, Uppaluri R, Lee JH, Vermeer PD. 2016. Metastatic model of HPV+ oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma demonstrates heterogeneity in tumor metastasis. Oncotarget. 7(17): 24194-207.
Storage and Stability
MLM cells should be stored in liquid nitrogen until use. The cells can be cultured for at least 10 passages after initial thawing without significantly affecting the cell marker expression and functionality.
Other Notes
This product is intended for sale and sold solely to academic institutions for internal academic research use per the terms of the “Academic Use Agreement” as detailed in the product documentation. For information regarding any other use, please contact licensing@milliporesigma.com.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.


![Anti-CD62E [ELAM-1] Antibody, clone 1.2B6 clone 1.2B6, from mouse](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/images/224/939/8a711839-25ef-4e45-badd-208503950c8a/640/8a711839-25ef-4e45-badd-208503950c8a.jpg)