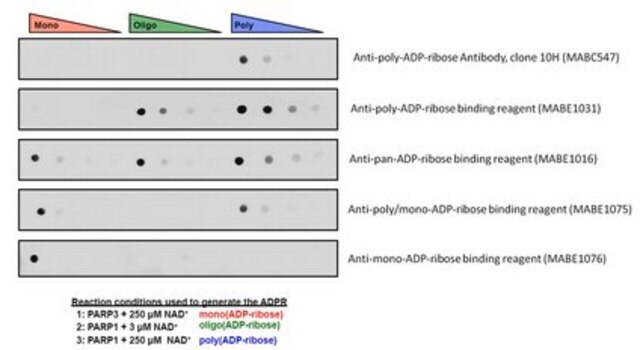
MABE1031
Anti-poly-ADP-ribose binding reagent
Anti-poly-ADP-ribose binding reagent is a reagent that selectively binds to ADP ribose for use in Western Blotting, Immunocytochemistry and Dot Blot.
Synonym(s):
poly-ADP-ribose binding reagent
About This Item
ICC
WB
immunocytochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
Recommended Products
biological source
Escherichia coli
Quality Level
antibody form
purified antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
species reactivity
human, mouse
species reactivity (predicted by homology)
all
technique(s)
dot blot: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
shipped in
dry ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
Specificity
Application
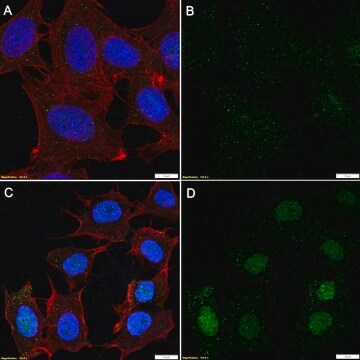
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected oligo(ADPR) and poly(ADPR)/PAR in 3T3-L1 cells (Lee Kraus, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center).
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
General Post-translation Modification
Quality
Western Blotting Analysis: This reagent detected oligo(ADPR) and poly(ADPR) on ADP-ribosylated PARP1 recombinant protein (Lee Kraus, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center).
Target description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Handling Recommendations: Upon receipt and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance.
Other Notes
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
PDSCL
Deleterious substance
JAN Code
MABE1031:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service