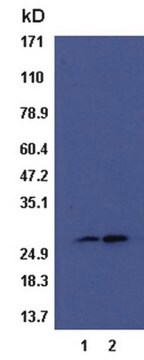
17-441
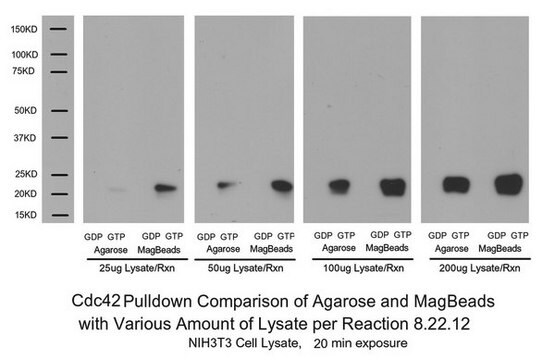
Rac1/Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit
The Rac1/Cdc42 Activation Assay provides an effective method for detecting Rac & Cdc42 activity in cell lysates.
Synonym(s):
Rac1 activation assay
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
species reactivity
human, mouse, rat
manufacturer/tradename
Upstate®
technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
affinity binding assay: suitable (G-protein)
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
Gene Information
human ... RAC1(5879)
General description
Specificity
Anti-Rac1, clone 23A8: Species Cross-reactivity: Human, mouse and rat. Other species cross-reactivity unknown.
Anti-cdc42 Species Cross-reactivity: Human, mouse, rat and dog. Other species cross-reactivity unknown.
Components
Anti-Rac1, clone 23A8, Catalog #05-389: One vial containing 250 μg of protein G purified mouse IgG2b in 250 μL of storage buffer (0.1 M Tris-glycine, pH 7.4, 0.15 M NaCl, containing 0.05% sodium azide).
Anti-cdc42, (mouse monoclonal IgG1) , Catalog # 05-542: One vial containing 50 μg of purified mouse IgG1 in 200 μL of 50% storage buffer (20 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1.5 mM sodium azide containing, 1 mg/mL BSA) and 50% glycerol.
Mg2+ Lysis/Wash Buffer, 5X, Catalog # 20-168 : Two vials, each vial containing 18 mL of 5X MLB: 125 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 750 mM NaCl, 5% Igepal CA-630, 50 mM MgCl2, 5 mM EDTA and 10% glycerol.
100X GTPγS, 10mM, Catalog # 20-176: One vial containing 50 μL of 10 mM GTPγS, 100X stock, in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.8, non-hydrolyzable analog of GTP. Sufficient to label 5 mL of cell lysates.
100X GDP, 100mM, Catalog # 20-177: One vial containing 50 μL of 100 mM GDP, 100X stock, in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.8. GDP (Guanosine 5′-Diphosphate) for in vitro labeling of G-proteins in the inactive form. Sufficient to label 5ml of cell lysates.
Quality
Storage and Stability
Legal Information
Disclaimer
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
17-441:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service