925802
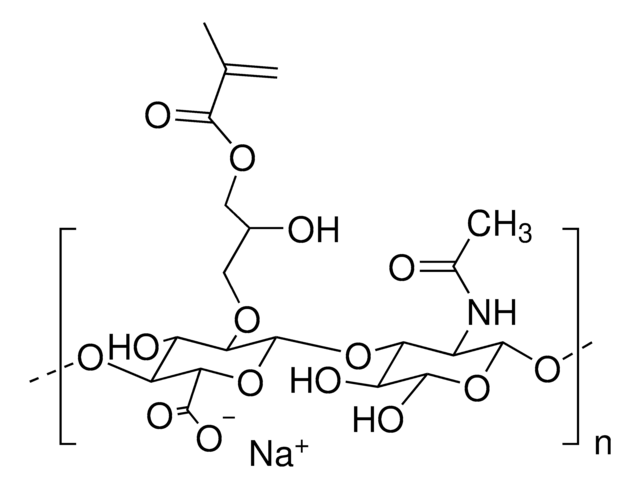
Silk fibroin
average mol wt 100 kDa (water soluble)
Synonym(s):
SilMA, Silk fibroin
About This Item
Recommended Products
mol wt
average mol wt 100 kDa (water soluble)
Quality Level
color
white to off-white
pH
6-8 (2% in water, when dissolved in water)
General description
Silk fibroin is used in biomedical applications due to its enhanced biocompatibility and biodegradability.
Silk fibroin (SF) demonstrates enhanced strength and stability compared to other common natural polymers due to its unique features including;
- amphiphilicity
- hydrophobicity
- substantial hydrogen bonding
- intrinsic low viscosity
- high protein crystallinity by ß-sheet crystals.
Application
Packaging
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
925802-BULK:
925802-1G:
925802-VAR:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service