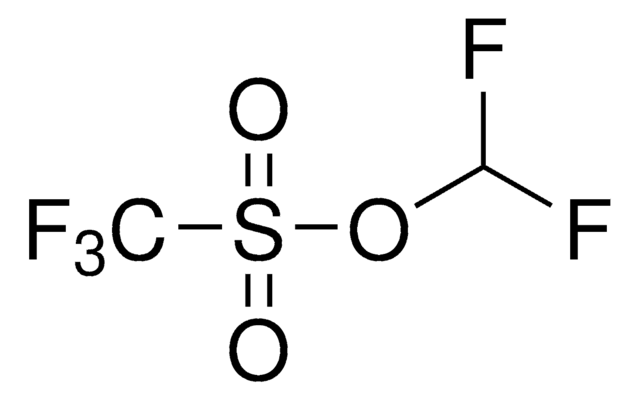
767840
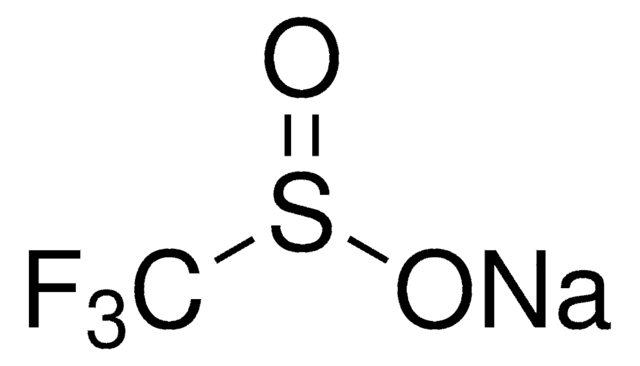
Zinc difluoromethanesulfinate
95%
Synonym(s):
Bis(((difluoromethyl)sulfinyl)oxy)zinc, 1,1-difluoro-methanesulfinic acid zinc salt (2:1), Baran difluoromethylation reagent, DFMS
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
95%
form
solid
reaction suitability
reaction type: C-C Bond Formation
reaction type: Fluorinations
reagent type: catalyst
reaction type: C-H Activation
reagent type: diversification reagent
functional group
fluoro
sulfinic acid
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
FC(F)S(=O)O[Zn]OS(=O)C(F)F
InChI
1S/2CH2F2O2S.Zn/c2*2-1(3)6(4)5;/h2*1H,(H,4,5);/q;;+2/p-2
InChI key
UGEYAPVLXKEKMP-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Practical and Innate Carbon-Hydrogen Functionalization of Heterocycles
DFMS is a new reagent for direct difluoromethylation of organic substrates via a radical process. This mild, operationally simple, chemoselective, and scalable difluoromethylation method is compatible with a range of nitrogen-containing heteroarene substrates of varying complexity as well as select classes of conjugated p−systems and thiols.†
A New Reagent for Direct Difluoromethylation
Learn More at the Professor and Product Portal of Professor Phil S. Baran.
Linkage
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
767840-VAR:
767840-100G:
767840-1KG:
767840-BULK:
767840-1G:
767840-10G:
767840-100MG:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The synthesis of heteroaromatic and aromatic compounds is at the heart of the chemical industry. The ever-growing demand for new chemical entities, coupled with dwindling resources and time constraints allotted to any given research project, a rapid way to diversify (hetero)aromatic scaffolds is needed.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service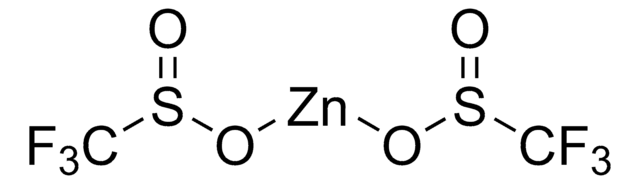

![Zinc di[bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide] 95%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/336/073/952daadd-0a7c-4bec-bbaf-442a24c62161/640/952daadd-0a7c-4bec-bbaf-442a24c62161.png)