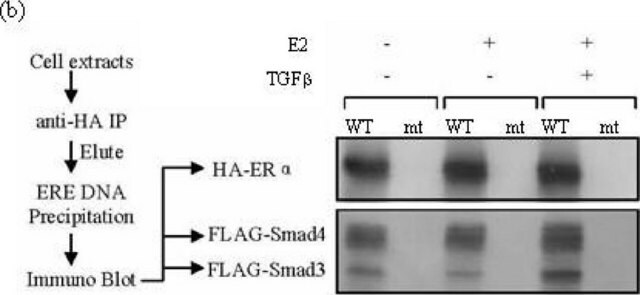
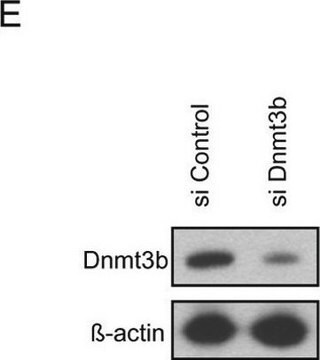
V8012
Anti-V5 antibody, Mouse monoclonal
clone V5-10, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Sinonimo/i:
V5 Tag Monoclonal Antibody, V5 antibody
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.56
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
mouse
Livello qualitativo
Coniugato
unconjugated
Forma dell’anticorpo
purified from hybridoma cell culture
Tipo di anticorpo
primary antibodies
Clone
V5-10, monoclonal
Concentrazione
~1 mg/mL
tecniche
immunocytochemistry: 1-2 μg/mL
western blot: 0.5-1 μg/mL
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Descrizione generale
Monoclonal Anti-V5 (mouse IgG1 isotype) is derived from the V5-10 hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from a BALB/c mouse immunized with a synthetic peptide conjugated to KLH.
The mouse monoclonal Anti-V5 antibody reacts specifically with the V5-tagged recombinant fusion proteins expressed in transfected mammalian cells or produced by in vitro translation.
The mouse mooclonal Anti-V5 antibody reacts specifically with the V5-taged recombinant fusion proteins expressed in transfected mammalian cells or produced by in vitro translation.
Specificità
Recognizes V5 Tag (GKPIPNPLLGLDST) fusion proteins
Stato fisico
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% bovine serum albumin and 15 mM sodium azide.
Stoccaggio e stabilità
For continuous use, store at 2-8 °C for up to one month. For extended storage, freeze in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing, or storage in "frost-free" freezers,is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify the solution by centrifugation before use. Working dilution samples should be discarded if not used within 12 hours.
Esclusione di responsabilità
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog, our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Non trovi il prodotto giusto?
Prova il nostro Motore di ricerca dei prodotti.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Sebastian Wissel et al.
G3 (Bethesda, Md.), 6(8), 2467-2478 (2016-06-10)
Traditional loss-of-function studies in Drosophila suffer from a number of shortcomings, including off-target effects in the case of RNA interference (RNAi) or the stochastic nature of mosaic clonal analysis. Here, we describe minimal in vivo GFP interference (miGFPi) as a
Daniel Ortuno et al.
F1000Research, 5, 137-137 (2016-03-22)
A common pathological hallmark of age-related neurodegenerative diseases is the intracellular accumulation of protein aggregates such as α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease, TDP-43 in ALS, and tau in Alzheimer's disease. Enhancing intracellular clearance of aggregation-prone proteins is a plausible strategy for
Ernesto Ciabatti et al.
Cell, 170(2), 382-392 (2017-07-12)
Neural networks are emerging as the fundamental computational unit of the brain and it is becoming progressively clearer that network dysfunction is at the core of a number of psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Yet, our ability to target specific networks
Blocking Double-Stranded RNA-Activated Protein Kinase PKR by Japanese Encephalitis Virus Nonstructural Protein 2A
Tu YC, et al.
Journal of Virology, 86(19), 10347-10358 (2012)
Xinjun Zhang et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 291(5), 2435-2443 (2015-12-04)
The Wnt family of secreted glycolipoproteins plays pivotal roles in development and human diseases. Tiki family proteins were identified as novel Wnt inhibitors that act by cleaving the Wnt amino-terminal region to inactivate specific Wnt ligands. Tiki represents a new
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.