SAB1103260
Anti-DCAF15 (567-580) antibody produced in rabbit
IgG fraction of antiserum
Sinonimo/i:
Anti-C19orf72, Anti-DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 15
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.41
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
rabbit
Coniugato
unconjugated
Forma dell’anticorpo
IgG fraction of antiserum
Tipo di anticorpo
primary antibodies
Clone
polyclonal
Stato
buffered aqueous solution
PM
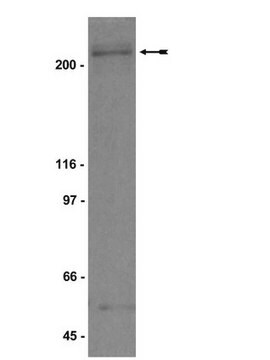
antigen ~66 kDa
Reattività contro le specie
human
tecniche
western blot: 1:500-1:2,000
N° accesso UniProt
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
modifica post-traduzionali bersaglio
unmodified
Informazioni sul gene
human ... DCAF15(90379)
Descrizione generale
DCAF15 (DNA damage binding protein1 (DDB1) and cullin4 (CUL4) associated factor 15) gene in human chromosome, is mapped to 19p13.12. DCAF15 lacks protein interaction domain.
DCAF15 protein is a substrate receptor for E3 ligase. This protein is a part of the cullin 4-RING (CRL4)-DCAF15 E3 ubiquitin ligase.
Immunogeno
synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acids 567-580 of human DCAF15
Applicazioni
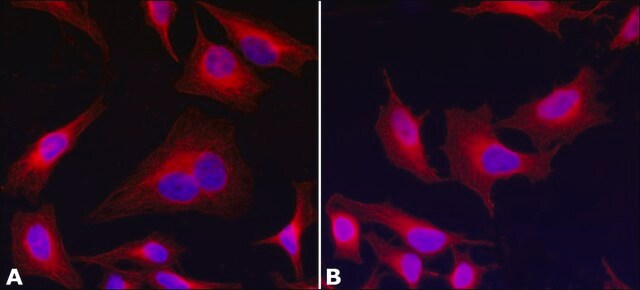
Anti-DCAF15 (567-580) antibody produced in rabbit has been used in western blotting.
Azioni biochim/fisiol
DCAF15 (DNA damage binding protein 1 (DDB1) and cullin4 (CUL4) associated factor 15) is the vertebrate ortholog of Saccharomyces pombe chromosome licensing and DNA replication factor 2 (Cdt2) and is required for destruction of Cdt1 during S phase and after DNA damage in human cells.
DCAF15 protein plays a role in RNA splicing and cell apoptosis of various cancer cell lines. This protein is also involved in ubiquitination and degradation of splicing factor RNA binding motif protein 39 (RBM39).
Stato fisico
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Esclusione di responsabilità
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Non trovi il prodotto giusto?
Prova il nostro Motore di ricerca dei prodotti.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Expanding the spectrum of rearrangements involving chromosome 19: A mild phenotype associated with a 19p13.12-p13. 13 deletion
Marangi G, et al.
American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A, 158(4), 888-893 (2012)
A family of diverse Cul4-Ddb1-interacting proteins includes Cdt2, which is required for S phase destruction of the replication factor Cdt1
Jin J, et al.
Molecular Cell, 23(5), 709-721 (2006)
Zhi Chen et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 1175-1175 (2017-04-28)
Cell cycle progression in mammals is strictly controlled by a number of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and CDK inhibitors (CKIs), the expression of which is often dysregulated in cancer cells. Our previous work revealed that Cullin 4B (CUL4B), a critical component
Xiao Dong et al.
Aging, 13(7), 10603-10618 (2021-04-10)
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is an evolutionarily conserved developmental program that has been implicated in tumorigenesis and confers metastatic properties upon cancer cells. ZEB1 is a master transcription factor that activates the EMT process in various cancers. ZEB1 is reportedly degraded
Tabitha C Ting et al.
Cell reports, 29(6), 1499-1510 (2019-11-07)
Indisulam and related sulfonamides recruit the splicing factor RBM39 to the CRL4-DCAF15 E3 ubiquitin ligase, resulting in RBM39 ubiquitination and degradation. Here, we used a combination of domain mapping and random mutagenesis to identify domains or residues that are necessary
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.