D8037
Driselase™ Basidiomycetes sp.
suitable for plant cell culture, BioReagent
Sinonimo/i:
Driselase™ from Basidiomycetes sp.
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Nome Commerciale
BioReagent
Stato
powder
Composizione
Protein, ≥10% biuret
tecniche
cell culture | plant: suitable
applicazioni
agriculture
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Applicazioni
Driselase™ Basidiomycetes sp. has been used:
- in spheroplast preparation from Coccomyxa cells
- in a CRISPR/Cas9-based mutagenesis protocol for Brachypodium distachyon and its allopolyploid relative, Brachypodium hybridum
- for cell wall digestion to perform whole-mount immunolocalization of Lotus japonicus root tissue
Azioni biochim/fisiol
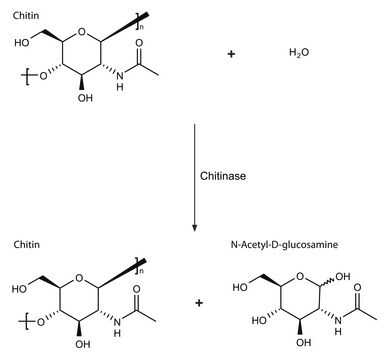
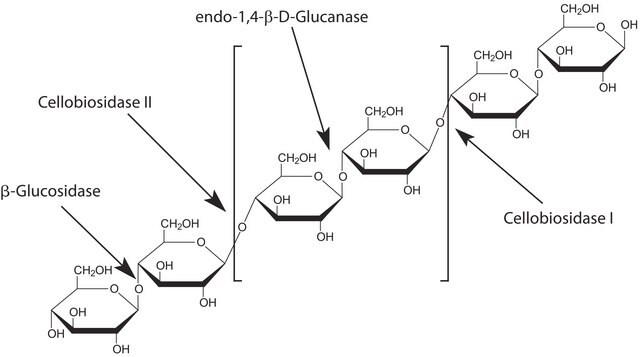
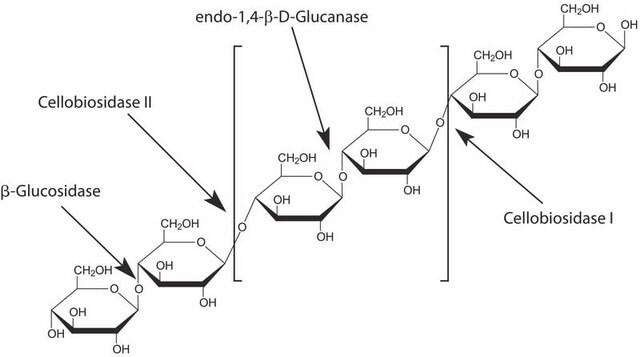
Driselase™ is a natural mixture of enzyme activities (fungal carbohydrates) used to digest plant cell walls to facilitate the maceration of plant materials, protoplast formation, and extraction processes. Driselase releases cell wall carbohydrates. This formulation contains enzyme activities of cellulose, endo-1,3-β-glucanase, and xylanase.
Altre note
Crude powder containing laminarinase, xylanase and cellulase.
Note legali
Driselase is a trademark of ASKA Animal Health Co. Ltd.
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Resp. Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
G J McDougall et al.
Carbohydrate research, 219, 123-132 (1991-10-14)
The retention times of 10 oligosaccharides, generated from the xyloglucans of Rosa and Tropaeolum by the action of Trichoderma cellulase, and of 17 related carbohydrates, in h.p.l.c. on an amino-substituted silica (Amino-Spheri-5) depended largely on the number of hydroxyl groups
M C Ralet et al.
Carbohydrate research, 263(2), 227-241 (1994-10-17)
Cell walls from sugar-beet pulp contain some feruloyl groups linked to the pectic neutral side-chains. Enzymic as well as chemical hydrolysis of the pulp yielded a series of feruloylated oligosaccharides, which have been purified by Sephadex LH-20 and Biogel P-2
Dieter Hackenberg et al.
Plant physiology, 172(2), 1154-1166 (2016-08-24)
In this study, we report the functional characterization of heterotrimeric G-proteins from a nonvascular plant, the moss Physcomitrella patens. In plants, G-proteins have been characterized from only a few angiosperms to date, where their involvement has been shown during regulation
Laura A Moody et al.
The New phytologist, 218(3), 1270-1277 (2018-03-03)
Forward genetics is now straightforward in the moss Physcomitrella patens, and large mutant populations can be screened relatively easily. However, perturbation of development before the formation of gametes currently leaves no route to gene discovery. Somatic hybridization has previously been
D T Kaplan et al.
Journal of nematology, 22(3), 399-406 (1990-07-01)
Radopholus spp. were reared in carrot tissue culture via established procedures, with slight modification. Several plant tissue maceration enzymes and flotation media (salts and sucrose) were evaluated with regard to nematode toxicity and extraction efficiency. Best extraction of viable nematodes
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.