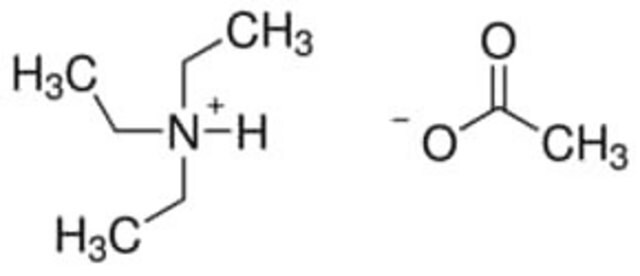
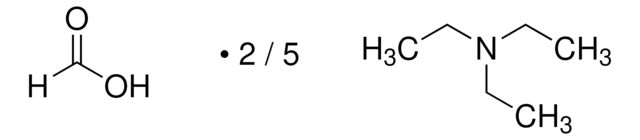90358
Triethylammonium acetate buffer
volatile buffer, ~1.0 M in H2O
Sinonimo/i:
Triethylammonium acetate buffer, Buffer solution 1 M pH 7.0 (volatile)
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
0.95—1.05 mol
Stato
liquid
Durata
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
Condizioni di stoccaggio
dry at room temperature
Concentrazione
1 M
~1.0 M in H2O
tecniche
electrophoresis: suitable
Colore
colorless
Indice di rifrazione
n20/D 1.357
pH
7.0
6.1
Densità
1.002 g/mL at 20 °C
Compatibilità
suitable for chromatography
suitable for protein modification
suitable for separation of small nucleic acid fragments
applicazioni
detection
diagnostic assay manufacturing
life science and biopharma
sample preparation
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C6H15N.C2H4O2/c1-4-7(5-2)6-3;1-2(3)4/h4-6H2,1-3H3;1H3,(H,3,4)
AVBGNFCMKJOFIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- as a buffer in proteomics studies
- as a component of the mobile phase to separate nucleotide sugars
- as a buffer for the separation of glycopeptides in proteomics research
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
- Suitable for Biological and Biochemical Research
- Ready available solution reduce the need for preparation time
Altre note
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.