51927
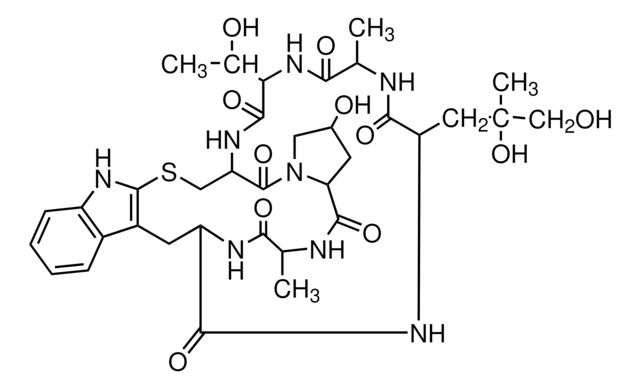
Phalloidin–Atto 594
suitable for fluorescence, ≥90.0% (HPLC)
Sinonimo/i:
Atto 594–Phalloidin
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
12352108
NACRES:
NA.32
Prodotti consigliati
Saggio
≥90.0% (HPLC)
Stato
solid
Produttore/marchio commerciale
ATTO-TEC GmbH
λ
in acetonitrile: water (3:7)
Assorbanza UV
λ: 600-606 nm Amax
Compatibilità
suitable for fluorescence
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Descrizione generale
Atto 594 is a novel fluorescent label belonging to the class of Rhodamine dyes. The dye is designed for application in the area of life science, e.g. labeling of DNA, RNA or proteins. Characteristic features of the label are strong absorption, high fluorescence quantum yield, high thermal and photo-stability, excellent water solubility, and very little triplet formation. After coupling to a substrate Atto 594 carries a net electrical charge of -1.
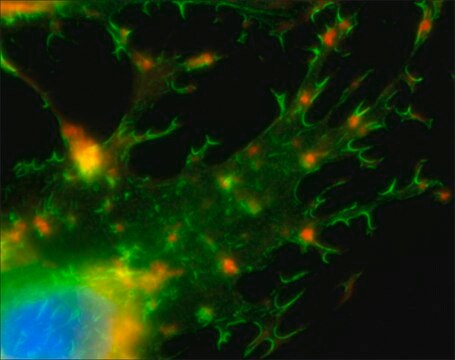
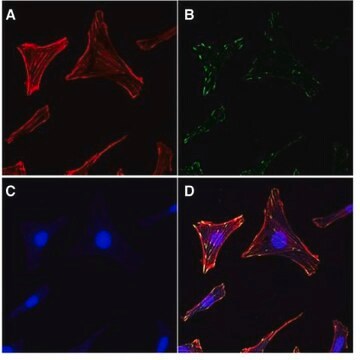
Phalloidin is a fungal toxin isolated from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides. Its toxicity is attributed to the ability to bind F actin in liver and muscle cells. As a result of binding phalloidin, actin filaments become strongly stabilized. Phalloidin has been found to bind only to polymeric and oligomeric forms of actin, and not to monomeric actin. The dissociation constant of the actin-phalloidin complex has been determined to be on the order of 3 x 10-8. Phalloidin differs from amanitin in rapidity of action; at high dose levels, death of mice or rats occurs within 1 or 2 hours. Fluorescent conjugates of phalloidin are used to label actin filaments for histological applications. Some structural features of phalloidin are required for the binding to actin. However, the side chain of amino acid 7 (g-d-dihydroxyleucine) is accessible for chemical modifications without appreciable loss of affinity for actin.
find more information here
Phalloidin is a fungal toxin isolated from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides. Its toxicity is attributed to the ability to bind F actin in liver and muscle cells. As a result of binding phalloidin, actin filaments become strongly stabilized. Phalloidin has been found to bind only to polymeric and oligomeric forms of actin, and not to monomeric actin. The dissociation constant of the actin-phalloidin complex has been determined to be on the order of 3 x 10-8. Phalloidin differs from amanitin in rapidity of action; at high dose levels, death of mice or rats occurs within 1 or 2 hours. Fluorescent conjugates of phalloidin are used to label actin filaments for histological applications. Some structural features of phalloidin are required for the binding to actin. However, the side chain of amino acid 7 (g-d-dihydroxyleucine) is accessible for chemical modifications without appreciable loss of affinity for actin.
find more information here
Confezionamento
Bottomless glass bottle. Contents are inside inserted fused cone.
Note legali
This product is for Research use only. In case of intended commercialization, please contact the IP-holder (ATTO-TEC GmbH, Germany) for licensing.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Anika M Helferich et al.
Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 75(23), 4301-4319 (2018-07-22)
Genetic and functional studies suggest diverse pathways being affected in the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), while knowledge about converging disease mechanisms is rare. We detected a downregulation of microRNA-1825 in CNS and extra-CNS system organs of both sporadic
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.