94904
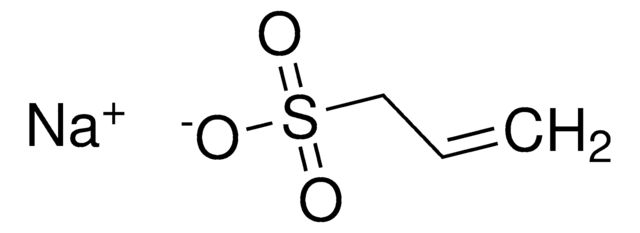
Sodium 4-vinylbenzenesulfonate
technical, ≥90% (T)
Sinonimo/i:
4-Vinylbenzenesulfonic acid sodium salt, Styrene-4-sulfonic acid sodium salt
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Grado
technical
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥90% (T)
Stato
powder
Punto di fusione
≥300 °C
Gruppo funzionale
sulfonic acid
Stringa SMILE
[Na+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)c1ccc(C=C)cc1
InChI
1S/C8H8O3S.Na/c1-2-7-3-5-8(6-4-7)12(9,10)11;/h2-6H,1H2,(H,9,10,11);/q;+1/p-1
XFTALRAZSCGSKN-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Categorie correlate
Applicazioni
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organi bersaglio
Respiratory system
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.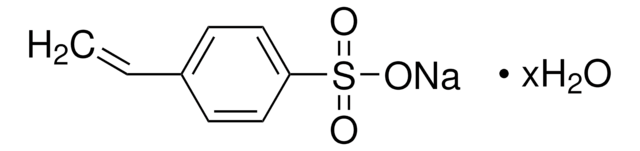
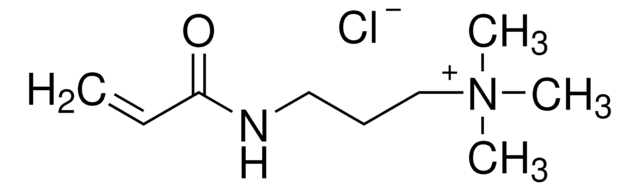
![[3-(Methacryloylamino)propyl]trimethylammonium chloride solution 50 wt. % in H2O](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/189/736/089bc8ae-2a98-416d-9f9a-a0a510b6b828/640/089bc8ae-2a98-416d-9f9a-a0a510b6b828.png)



![[2-(Acryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethylammonium chloride solution 80 wt. % in H2O, contains 600 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/393/326/f7e19585-5431-4220-81b5-f458de6d63d0/640/f7e19585-5431-4220-81b5-f458de6d63d0.png)
![[2-(Methacryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethylammonium chloride solution 75 wt. % in H2O](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/316/612/66b0f4cf-d060-427d-b4f5-e8fab3e5cffe/640/66b0f4cf-d060-427d-b4f5-e8fab3e5cffe.png)