930903
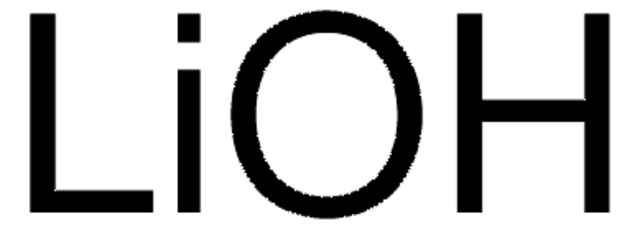
Lithium hydroxide monohydrate
battery grade, ≥99.9% trace metals basis
Sinonimo/i:
Lithine hydrate, Lithium hydroxide hydrate
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Grado
battery grade
Saggio
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Forma fisica
powder
Caratteristiche più verdi
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Impurezze
≤1000 ppm (trace metals analysis)
Punto di fusione
423 °C
Solubilità
H2O: soluble ((lit.))
ethanol: slightly soluble ((lit.))
methanol: soluble ((lit.))
Anioni in tracce
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤50 ppm
applicazioni
battery manufacturing
Categoria alternativa più verde
Stringa SMILE
[Li+].O.[OH-]
InChI
1S/Li.2H2O/h;2*1H2/q+1;;/p-1
GLXDVVHUTZTUQK-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Lithium hydroxide is produced in several ways. Most commonly, lithium carbonate is reacted with calcium hydroxide in a metathesis reaction. This directly yields lithium hydroxide hydrate, which is separated from the insoluble calcium carbonate byproduct and purified. Alternatively, when the source of lithium is spodumene ore, the ore can be converted to lithium hydroxide without first forming the carbonate. In the process, the lithium ore is treated with high-temperatures and sulfuric acid to form lithium sulfate; then the lithium sulfate is reacted with sodium hydroxide to form lithium hydroxide hydrate, which is purified.
Applicazioni
Our battery grade lithium hydroxide monohydrate is well-suited for synthesis of nickel-rich metal oxides, like lithium nickel-manganese-aluminum oxide (NMA) and complex quaternary transition metal oxides like Zr-doped or Ti-doped nickel-manganese oxide.
Our lithium hydroxide monohydrate can also be used to synthesize lithium iron phosphates like LiFePO4 or lithium manganese oxides like Li2Mn2O4.
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Ci dispiace, ma al momento non ci sono COA disponibili online per questo prodotto.
Se ti serve aiuto, non esitare a contattarci Servizio Clienti
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.