927651
TissueFab® bioink kit
(Gel)ma Fibrin (UV/365), low endotoxin
Sinonimo/i:
Fibrin, Fibrinogen, GelMA, Gelatin methacrylamide, Gelatin methacrylate, Gelatin methacryloyl, Thrombin
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Descrizione
HNMR in D2O at 40°C
Livello qualitativo
Stato
(Solid chunks, fibers or powder)
Impurezze
<10 CFU/g Bioburden (Fungal)
<10 CFU/g Bioburden (Total Aerobic)
<125 EU/g Endotoxin
Colore
white
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
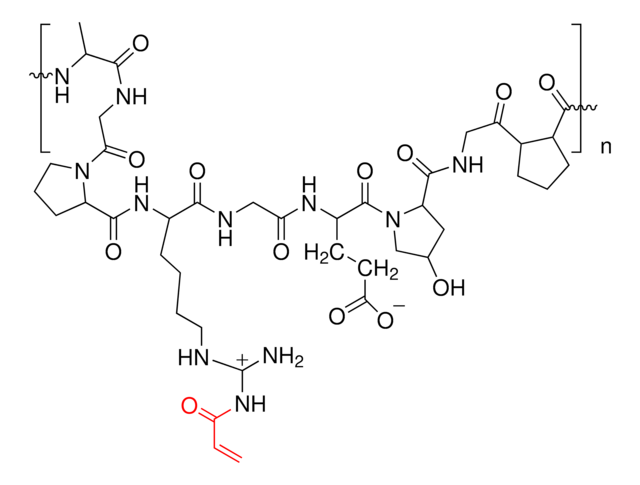
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
The protocol can be found under "More Documents" at the bottom of the page.
TissueFab® bioink kit- (Gel)ma Fibrin (UV/365), low endotoxin contains:
2- 500 mg lyophilized ink components
1- lyophilized thrombin powder
1- 10 ml HEPES buffer.
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
Low Endotoxin, low bioburden: Endotoxins have been demonstrated negatively impact cellular growth, morphology, differentiation, inflammation and protein expression. Bioburden is defined as the number of contaminated organisms found in a given amount of material. We test each lot for endotoxins as well as total bioburden (aerobic and fungal) to minimize unwanted interactions. For more information: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/technical-documents/technical-article/microbiological-testing/pyrogen-testing/what-is-endotoxin
Note legali
Prodotti correlati
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organi bersaglio
Respiratory system
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documenti section.
Se ti serve aiuto, non esitare a contattarci Servizio Clienti
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.