SRP0158
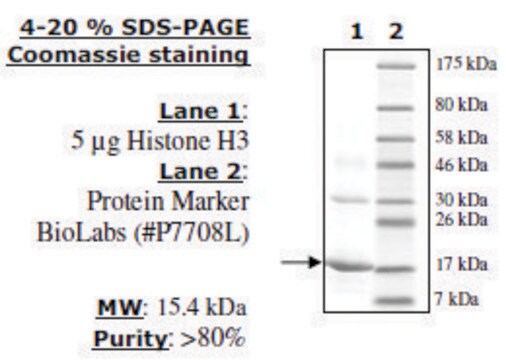
Histone H3 (2-58) human
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥70% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonym(s):
HIST1H3E, Histone H3.1
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Assay
≥70% (SDS-PAGE)
form
aqueous solution
mol wt
32 kDa
packaging
pkg of 500 μg
storage condition
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
concentration
>0.02 mg/mL
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
human ... HIST1H3E(8353)
General description
Human Histone 3 (GenBank Accession No. NM_003532), (amino acid 2-58) with N-terminal GST tag, MW = 32kDa, expressed in an Escherichia coli expression system.
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical form
Preparation Note
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Epigenetic modifications are thought to occur through two key interconnected processes—DNA methylation and the covalent modification of histones.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service