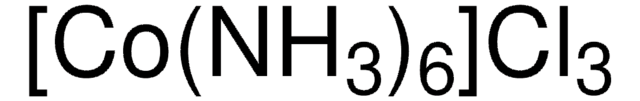H7891
Hexammine cobalt(III) chloride
for use in transformations, X-ray crystallography and NMR
Synonym(s):
Cobalt hexammine trichloride, Hexaamminecobalt trichloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
[Co(NH3)6]Cl3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
267.48
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.52
Recommended Products
grade
for molecular biology
Quality Level
form
powder
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
N.N.N.N.N.N.[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Co+3]
InChI
1S/3ClH.Co.6H3N/h3*1H;;6*1H3/q;;;+3;;;;;;/p-3
InChI key
JXBGZYGSWFSYFI-UHFFFAOYSA-K
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Hexammine cobalt(III) is considered an analog of fully solvated magnesium, capable of activating some enzymes that requires magnesium. It is useful in DNA condensation studies.
Application
Suitable for
- DNA condensation studies
- induction of transitions of DNA from B to A or Z forms
- induction of nucleic acid crystal growth
- stabilization of tertiary tRNA interactions
- preparation of ligation buffer
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 4 - Carc. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Christine C Conwell et al.
Biochemistry, 43(18), 5380-5387 (2004-05-05)
Millimolar concentrations of divalent cations are shown to affect the size of toroids formed when DNA is condensed by multivalent cations. The origins of this effect were explored by varying the order in which MgCl(2) was added to a series
Pinpinat Malaikaew et al.
Journal of photochemistry and photobiology. B, Biology, 103(3), 251-255 (2011-05-03)
In this study, a new small-molecule-based reagent was designed to recognize and bind to specific site in protein. A new pyrenyl probe, d-biotinyl-1(1-pyrene)methylamide (Py-biotin) was designed and synthesized by coupling of d-biotin to 1(1-pyrene)methylamine hydrochloride. Binding studies and site-specific photocleavage
T Allers et al.
Nucleic acids research, 28(2), e6-e6 (1999-12-22)
The Holliday junction is a central intermediate in genetic recombination. This four-stranded DNA structure is capable of spontaneous branch migration, and is lost during standard DNA extraction protocols. In order to isolate and characterize recombination intermediates that contain Holliday junctions
M C Whitby et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 273(31), 19729-19739 (1998-07-25)
The RecG protein of Escherichia coli is a junction-specific DNA helicase that drives branch migration of Holliday intermediates in genetic recombination and DNA repair. The reaction was investigated using synthetic X-junctions. RecG dissociates X-junctions to flayed duplex products, although DNA
Meredith Newby Lambert et al.
RNA (New York, N.Y.), 11(11), 1688-1700 (2005-10-26)
Helix (H)27 from Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal (r)RNA is centrally located within the small (30S) ribosomal subunit, immediately adjacent to the decoding center. Bacterial 30S subunit crystal structures depicting Mg(2+) binding sites resolve two magnesium ions within the vicinity of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service