07270
Methyl 6-aminohexanoate hydrochloride
≥99.0% (AT)
Synonym(s):
Methyl 6-aminocaproate hydrochloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
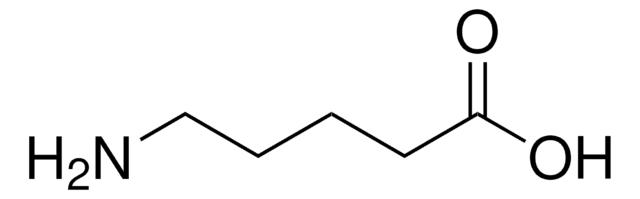
NH2(CH2)5COOCH3 · HCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
181.66
Beilstein:
3687692
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.0% (AT)
form
powder or crystals
reaction suitability
reaction type: solution phase peptide synthesis
color
white
mp
117-124 °C
application(s)
peptide synthesis
SMILES string
Cl.COC(=O)CCCCCN
InChI
1S/C7H15NO2.ClH/c1-10-7(9)5-3-2-4-6-8;/h2-6,8H2,1H3;1H
InChI key
YSLDOTFAFZJPOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Methyl 6-aminohexanoate hydrochloride also known as Methyl 6-aminocaproate hydrochloride, is commonly used in the solution-phase peptide synthesis.
Application
Methyl 6-aminohexanoate hydrochloride is used to synthesize papain-catalyzed peptides.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Papain-catalyzed synthesis of polyglutamate containing a nylon monomer unit
K Yazawa, et.al.
Polymers, 8, 194-194 (2016)
Petr Chytil et al.
Molecular pharmaceutics, 15(9), 3654-3663 (2018-03-16)
Herein, the biodegradable micelle-forming amphiphilic N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide (HPMA)-based polymer conjugates with the anticancer drug doxorubicin (Dox) designed for enhanced tumor accumulation were investigated, and the influence of their stability in the bloodstream on biodistribution, namely, tumor uptake, and in vivo
Tomáš Etrych et al.
European journal of pharmaceutical sciences : official journal of the European Federation for Pharmaceutical Sciences, 58, 1-12 (2014-03-19)
In this study, we describe the synthesis, physico-chemical characterisation and results of the in vitro and in vivo evaluation of the biological behaviour of N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide-based (HPMA) copolymer conjugates bearing doxorubicin (DOX) partly bound via a pH-sensitive hydrazone and partly via
Martin Studenovský et al.
Anticancer research, 35(2), 753-757 (2015-02-11)
In the present study, we describe the synthesis and physicochemical properties of a novel pH- and thermoresponsive micellar drug delivery system for an anticancer ellipticinium derivative based on the triblock copolymer poly(ethylene oxide)-block-[tert-butylacrylamide-co-6-(N-methacryloylamino)hexanoic acid hydrazide]-block-poly(ethylene oxide). The system was designed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service