47634
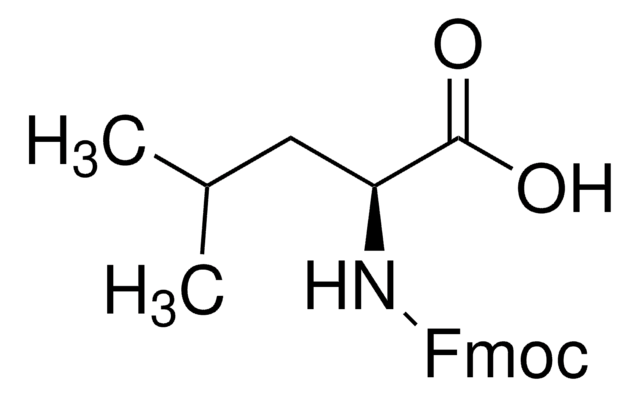
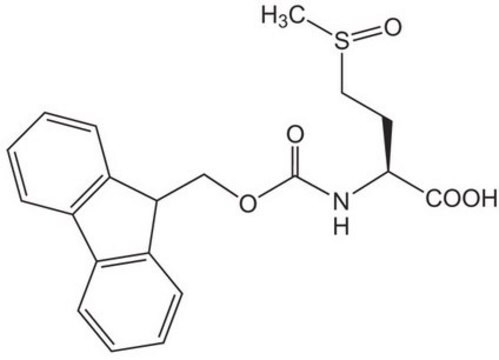
Fmoc-Met-OH
≥98.0% (HPLC), for peptide synthesis
Synonym(s):
Fmoc-L-methionine
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Fmoc-Met-OH, ≥98.0% (HPLC)
Quality Level
Assay
≥98.0% (HPLC)
optical activity
[α]20/D -29.5±1.5°, c = 1% in DMF
reaction suitability
reaction type: Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis
mp
121-123 °C (lit.)
application(s)
peptide synthesis
functional group
Fmoc
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
CSCC[C@H](NC(=O)OCC1c2ccccc2-c3ccccc13)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C20H21NO4S/c1-26-11-10-18(19(22)23)21-20(24)25-12-17-15-8-4-2-6-13(15)14-7-3-5-9-16(14)17/h2-9,17-18H,10-12H2,1H3,(H,21,24)(H,22,23)/t18-/m0/s1
InChI key
BUBGAUHBELNDEW-SFHVURJKSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service