268542
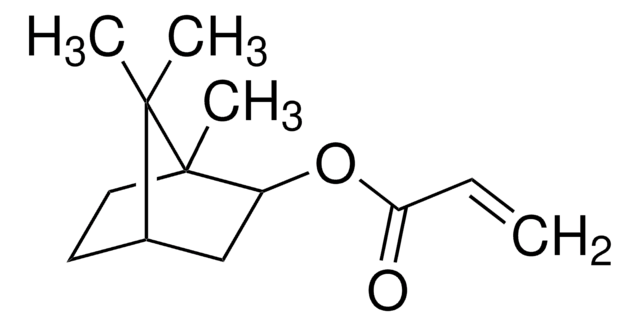
Hydroxypropyl methacrylate
Mixture of hydroxypropyl and hydroxyisopropyl methacrylates, 97%, contains 180-220 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
Synonym(s):
HPMA
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor density
>1 (vs air)
vapor pressure
0.05 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Assay
97%
form
liquid
contains
180-220 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
refractive index
n20/D 1.447 (lit.)
bp
57 °C/0.5 mmHg (lit.)
density
1.066 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
CC(=C)C(=O)OCCCO
InChI
1S/C7H12O3/c1-5(2)7(9)10-6(3)4-8/h6,8H,1,4H2,2-3H3
InChI key
ZMARGGQEAJXRFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- Synthesis of poly hydroxypropyl methacrylate cryogel incorporated with Zn/Ce substituted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for rejuvenation of femoral fracture: This study explores the synthesis of a cryogel incorporating hydroxypropyl methacrylate and Zn/Ce substituted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, aimed at bone fracture healing (H Zhou, H Jiao, J Xu, Y Liu, S Wei, 2019).
- Poly(Hydroxypropyl methacrylate-co-glycidyl methacrylate): Facile synthesis of well-defined hydrophobic gels containing hydroxy-functional methacrylates: This article presents the synthesis of hydrophobic gels using hydroxypropyl methacrylate and glycidyl methacrylate, useful in various material applications (N Orakdogen, B Sanay, 2017).
- Initiated chemical vapor deposition of poly(Hydroxypropyl methacrylate) thin films: The study covers the chemical vapor deposition process for creating thin films of poly(hydroxypropyl methacrylate) on membranes, enhancing their functional properties (E Sevgili, M Karaman, 2019).
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Carc. 1B - Eye Irrit. 2 - Muta. 1B - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
203.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
95 °C - closed cup
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service