220515
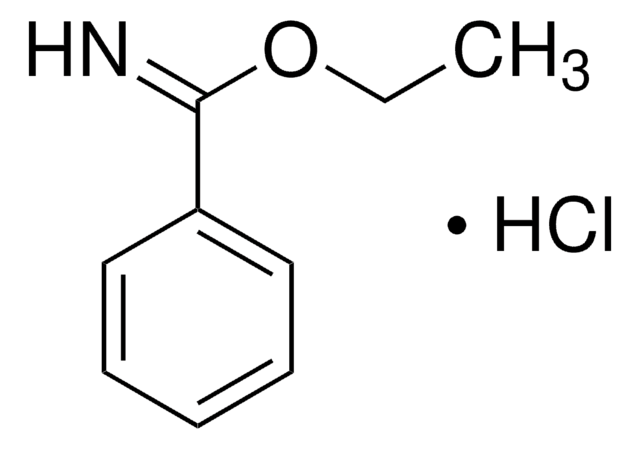
Methyl benzimidate hydrochloride
97%
Synonym(s):
Benzimidoic acid methyl ester hydrochloride, Methyl benzenecarboximidate hydrochloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
C6H5C(=NH)OCH3·HCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
171.62
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
97%
mp
105-107 °C (dec.) (lit.)
functional group
ether
phenyl
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl.COC(=N)c1ccccc1
InChI
1S/C8H9NO.ClH/c1-10-8(9)7-5-3-2-4-6-7;/h2-6,9H,1H3;1H
InChI key
HDJNHVNQRJMWSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
Methyl benzimidate hydrochloride was used:
- in the synthesis of chiral phenyldihydroimidazole derivative
- as imidating reagent to modify Lys residues of cyclic Lys-Gly-Asp peptide to afford acetimidate analogs
- in the synthesis of N-benzimidoyl-(1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine)
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
R M Scarborough et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 268(2), 1066-1073 (1993-01-15)
Members of the snake venon-derived, "disintegrin" peptide family containing the Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) amino acid sequence are among the most potent inhibitors of the binding of adhesive proteins to platelet glycoprotein (GP) IIb-IIIa. However, GPIIb-IIIa antagonists containing the RGD sequence are
J Einsiedel et al.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 11(18), 2533-2536 (2001-09-11)
Conformationally restricted benzamide bioisosteres were investigated when the chiral phenyldihydroimidazole derivative 4e (FAUC 179) showed strong and highly selective dopamine D4 receptor binding (K(i)high=0.95nM). Mitogenesis experiments indicated partial agonist properties (42%). EPC syntheses of the target compounds of type 4
Tao Ji et al.
Chemical research in toxicology, 20(4), 701-708 (2007-03-27)
Thiobenzamide (TB) is hepatotoxic in rats causing centrolobular necrosis, steatosis, cholestasis, and hyperbilirubinemia. It serves as a model compound for a number of thiocarbonyl compounds that undergo oxidative bioactivation to chemically reactive metabolites. The hepatotoxicity of TB is strongly dependent
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service