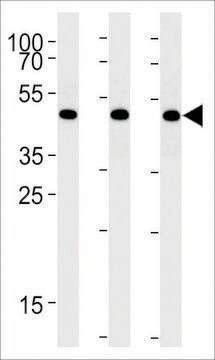
General description
The gene for angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) is mapped to human chromosome Xp22.2. This protein is the first known human homologue of ACE. ACE2 has been identified from 5′ sequencing of a human heart failure ventricle cDNA library. It contains a signal peptide, one metalloprotease active site and a transmembrane domain. ACE-2 is a secreted and an integral membrane protein. It is expressed predominantly on the endothelium.
Application
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2) has been used in the ACE-2 inhibition assays for inhibitor selectivity studies. It has also been used for identifying potent ACE2-blocking monoclonal antibodies in an on-chip assay and in human-ACE2-blocking assay using a biolayer interferometry biosensor. This approach serves for rational vaccine designing and for the selection of robust immunotherapeutic agents against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection.
Biochem/physiol Actions
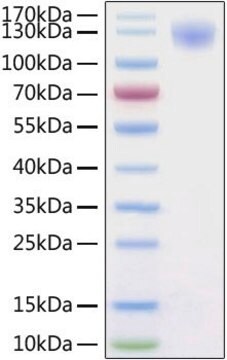
Recombinant human Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE-2) is expressed in human HEK 293 cells as a C-terminally flag and histidine-tagged glycoprotein with a calculated molecular mass of 85.9 kDa (amino acids Gln18-Ser740, with a C-terminal 10-His tag). The DTT-reduced protein migrates as a 90-120 kDa polypeptide on SDS-PAGE due to glycosylation. This protein is manufactured in human cells, with no serum. The human cells expression system allows human-like glycosylation and folding, and often supports higher specific activity of the protein.
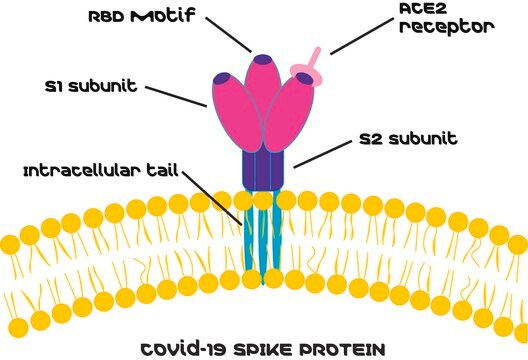
The angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) functions as carboxydipeptidase. The central role of ACE-2, is to counter ACE activity by reducing the bioavailability of angiotensin (Ang)-II and increasing the Ang(1-7) formation. ACE-2 is a part of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Many researches show that Ace-2 ensures the protection of peripheral tissues and might be efficient to treat RAS-related diseases. Also, an imbalance in Ace-2/Ang-(1-7) and ACE/Ang-II axes is important for the onset of cardiovascular diseases. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and human coronavirus (HCoV)-NL63 infection viruses has been shown to use its surface protein spike (glycoprotein) to bind to human ACE-2 receptor. The S protein is cleaved into subunits, S1 and S2 during the COVID-19 infection. S1 contains the receptor binding domain (RBD) which enables coronaviruses to bind to the peptidase domain (PD) of ACE2. Thus, ACE2 has become a high focus research target for COVID-19 infection.
Unit Definition
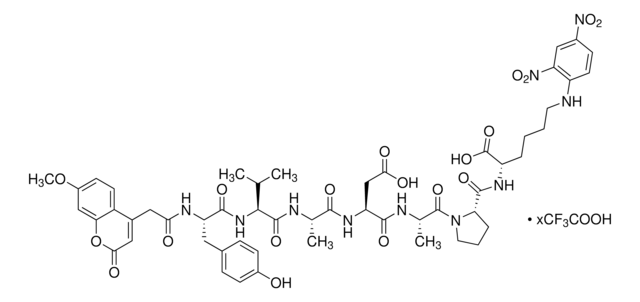
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme required to cleave 1 picomole of the fluorogenic peptide substrate, Mca-YVADAPK(Dnp)-OH in one minute, in 37 °C, pH 7.5.
Physical form
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH7.4.