P9120
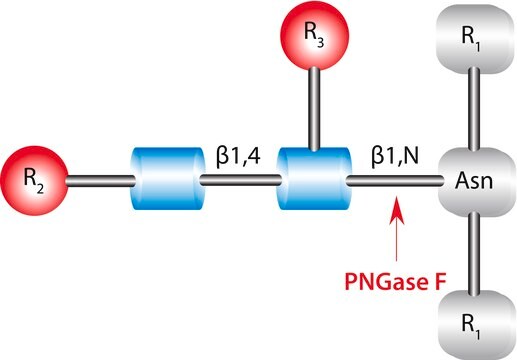
PNGase F from Elizabethkingia meningoseptica
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, set of 100 units nanomolar unit
Synonym(s):
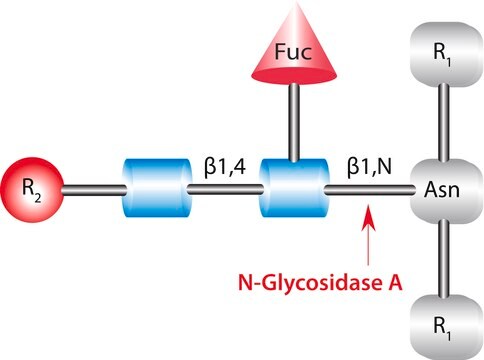
N-Glycanase®, N-Glycosidase F, PNGase F from Chryseobacterium meningosepticum, PNGase F from Flavobacterium meningosepticum, Peptide N-glycosidase
About This Item
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Quality Level
conjugate
(N-linked)
specific activity
≥10 units/mg protein
mol wt
36 kDa
packaging
set of 100 units nanomolar unit
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- of recombinant soybean agglutinin (rSBA) in Nicotiana benthamiana (NbrSBA) and Solanum tuberosum (StrSBA)
- of frontal cortical lysate to verify the glycosylation profile of β-secretase (BACE proteins)
- of cell lysate for evaluating the siRNA silencing of cellular prion protein (PrPc) post transfection
Biochem/physiol Actions
Packaging
Unit Definition
Legal Information
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Repr. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
N-Linked Glycan Strategies.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service