G6511
Glutathione S-Transferase from equine liver
lyophilized powder, ≥25 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
GST, Glutathione R-transferase, Glutathione S-alkenetransferase, Glutathione S-alkyltransferase, Glutathione S-aralkyltransferase, Glutathione S-aryltransferase, Glutathione S-epoxidetransferase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.47
Recommended Products
biological source
equine liver
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥25 units/mg protein
mol wt
45-50 kDa
composition
Protein, ≥60%
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Glutathione S-transferase (GST) is a major detoxification enzyme, and exists as multiple cytoplasmic and membrane-bound isozymes. These isozymes differ in their catalytic activity, as well as in their non-catalytic binding properties. Cytoplasmic isoforms of GST are encoded by five genes, namely α, θ, μ, σ and π. α, μ and π are the most abundant forms in mammals. Membrane bound GST forms are encoded by a single gene.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Glutathione S-transferase (GST) from equine liver has been used-
- as a constituent of Tris buffer for incubation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) with atracurium to assess the proliferation of HUVEC in the presence of atracurium
- as a component of GSB stock solution to determine GSB (glutathione S-bimane) conjugate fluorescence intensity in intact Arabidopsis cells
- as an enzyme standard in spectrophotometric assay to determine the activity of GST
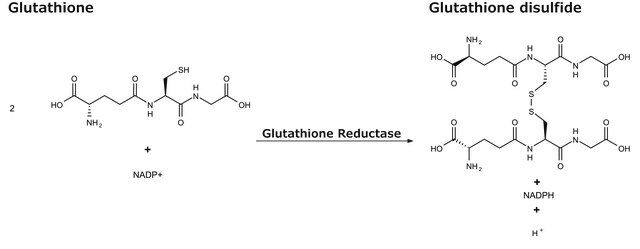
Glutathione S-transferases are a family of proteins that catalyze the conjugation of reduced glutathione with a variety of hydrophobic chemicals containing electrophilic centers.
Unit Definition
One unit will conjugate 1.0 μmole of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene with reduced glutathione per min at pH 6.5 at 25°C.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder containing Tris, reduced glutathione and EDTA.
Analysis Note
Protein determined by biuret.
Purified and assayed by a modification of the method of Simons and Vander Jagt.
Enzymatic activities are based on the conjugation of reduced glutathione with a second substrate. The individual proteins generally have activity with more than one class of substrate.
Purified and assayed by a modification of the method of Simons and Vander Jagt.
Enzymatic activities are based on the conjugation of reduced glutathione with a second substrate. The individual proteins generally have activity with more than one class of substrate.
inhibitor
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
A Amann et al.
Anesthesia and analgesia, 93(3), 690-696 (2001-08-29)
We tested the influence of atracurium and cisatracurium (final concentrations: 0, 0.96, 3.2, 9.6, 32, and 96 microM) on proliferation of human cells (hepatoma HepG2 cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells) in vitro. In additional experiments, glutathione, N-acetylcysteine, or
Molecular cloning and characterization of a Glutathione S-transferase gene from Hessian fly (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae)
Yoshiyama M and Shukle R H
Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 97(6), 1285-1293 (2004)
Melissa P Mezzari et al.
Plant physiology, 138(2), 858-869 (2005-06-01)
Understanding the function of detoxifying enzymes in plants toward xenobiotics is of major importance for phytoremediation applications. In this work, Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana; ecotype Columbia) seedlings were exposed to 0.6 mm acetochlor (AOC), 2 mm metolachlor (MOC), 0.6 mm 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene
J D Hayes et al.
Critical reviews in biochemistry and molecular biology, 30(6), 445-600 (1995-01-01)
The glutathione S-transferases (GST) represent a major group of detoxification enzymes. All eukaryotic species possess multiple cytosolic and membrane-bound GST isoenzymes, each of which displays distinct catalytic as well as noncatalytic binding properties: the cytosolic enzymes are encoded by at
Piotr Jakubowski et al.
Toxicology and applied pharmacology, 269(1), 34-42 (2013-03-19)
Snake venom antagonists of α2β1 integrin have been identified as members of a C-lectin type family of proteins (CLP). In the present study, we characterized three new CLPs isolated from Echis sochureki venom, which interact with this integrin. These proteins
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service