F2928
Monoclonal Anti-Fas Ligand antibody produced in rat
clone 101624, purified immunoglobulin, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Anti-CD95L, Anti-FasL
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rat
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
101624, monoclonal
form
lyophilized powder
species reactivity
mouse
technique(s)
neutralization: suitable
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL
isotype
IgG1
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
mouse ... Fasl(14103)
General description
Fas Ligand is a 40kDa type II membrane protein, which also known as FasL and CD95L, belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family. In the new TNF superfamily nomenclature, FasL is referred as TNFSF6. It consists of TNFα, α and β chains of lymphotoxin (LT), CD40 ligand, and CD30 ligand. It also has four potential N-glycosylation sites which appear to be variably used.
Immunogen
purified recombinant mouse Fas Ligand, amino acids 132-279, expressed in NSO cells.
Application
The monoclonal Anti-Fas Ligand antibody is suitable for western blot analysis of rat thymus homogenates to detect the recombinant rFasL molecule. The antibody is also suitable for immunoblotting at a concentration of 1-2μg/ml and ELISA at a concentration of 0.5-1.0μg/ml.
Biochem/physiol Actions
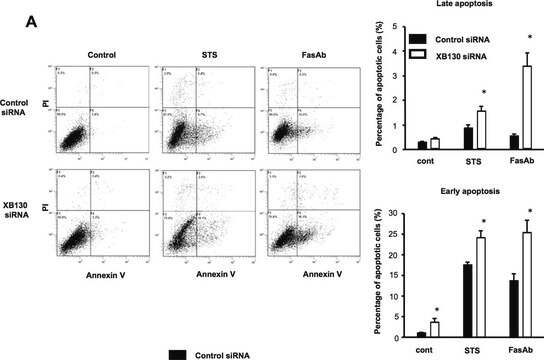
FasL is predominantly expressed on activated T cells and NK cells, whereas Fas is expressed on various cell types. The gene expression is induced by the activation of mature T cells with phorbol myristic acetate (PMA) and ionomycin, concanavalin A (Con A) or anti-CD3. After cleaving of FasL, it can generate the soluble Fas ligand, a non-covalently linked homotrimer. Membrane-bound FasL and TNFα are primary activators of their receptors. Soluble FasL may inhibit the killing effect of membrane FasL. It plays an important role in modulating immune response by inducing cell apoptosis to maintain homeostasis, self-tolerance of lymphocytes, and immune privilege. It has chemoattractant characteristics for neutrophils which indicate proinflammatory function.
Physical form
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in phosphate buffered saline containing carbohydrates.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
S Sieg et al.
Journal of virology, 70(12), 8747-8751 (1996-12-01)
Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are common human pathogens. In this report we demonstrate the capacity of HSV-2, but not HSV-1, to inhibit the activity and cell surface expression of Fas ligand, an important molecule
T Suda et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 154(8), 3806-3813 (1995-04-15)
Fas ligand (FasL) is a membrane-type cytokine belonging to the TNF family, and induces apoptosis through its cell-surface receptor, Fas. To determine the cell types that express FasL, various mouse tissues and cell lines were examined by Northern hybridization using
M G Cifone et al.
The Journal of experimental medicine, 180(4), 1547-1552 (1994-10-01)
Intracellular pathways leading from membrane receptor engagement to apoptotic cell death are still poorly characterized. We investigated the intracellular signaling generated after cross-linking of CD95 (Fas/Apo-1 antigen), a broadly expressed cell surface receptor whose engagement results in triggering of cellular
Gabriella Brunlid et al.
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio), 25(10), 2551-2558 (2007-07-07)
The potential of pluripotent embryonic stem (ES) cells to develop into functional cells or tissue provides an opportunity in the development of new therapies for many diseases including neurodegenerative disorders. The survival of implanted cells usually requires systemic immunosuppression, however
A Oehm et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 267(15), 10709-10715 (1992-05-25)
The APO-1 antigen as defined by the mouse monoclonal antibody anti-APO-1 was previously found to be expressed on the cell surface of activated human T and B lymphocytes and a variety of malignant human lymphoid cell lines. Cross-linking of the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service