C8271
Cytidine-5′-monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid sodium salt
≥85% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
CMP-NAN, CMP-NANA, CMP-Neu5Ac, CMP-Sialic acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic (organic)
Quality Level
Assay
≥85% (HPLC)
form
powder
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
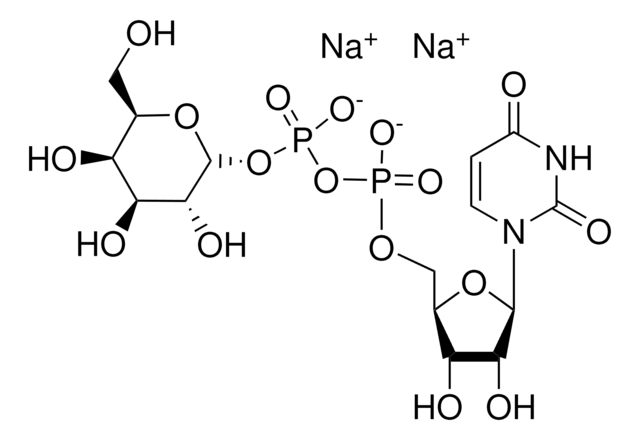
[Na+].CC(=O)N[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)C[C@@](O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO)(OP([O-])(=O)OC[C@H]2O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]2O)N3C=CC(N)=NC3=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C20H31N4O16P.Na/c1-7(26)22-12-8(27)4-20(18(32)33,39-16(12)13(29)9(28)5-25)40-41(35,36)37-6-10-14(30)15(31)17(38-10)24-3-2-11(21)23-19(24)34;/h2-3,8-10,12-17,25,27-31H,4-6H2,1H3,(H,22,26)(H,32,33)(H,35,36)(H2,21,23,34);/q;+1/p-1/t8-,9+,10+,12+,13+,14+,15+,16?,17+,20+;/m0./s1
InChI key
VFRHSOGUONIUOR-CTFMUGKASA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- as a standard in high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAEC-PAD) for nucleotide sugar analysis in Joubert syndrome type 10 (JBTS10) patient cells and control skin fibroblasts,
- As a substrate for the enzymatic sialylation of G2 glycoforms, resialylation assay,
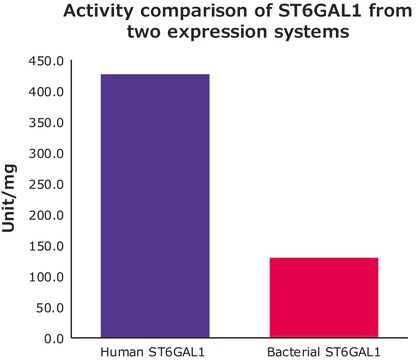
- in in-vitro sialyltransferase assay
Biochem/physiol Actions
Preparation Note
CMP-NAN is very acid-labile.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The presence of multiple functional groups and stereocenters in complex carbohydrates makes them challenging targets for the organic chemist.
Glycosyltransferases were initially considered to be specific for a single glycosyl donor and acceptor, which led to the one enzyme-one linkage concept. Subsequent observations have refuted the theory of absolute enzymatic specificity by describing the transfer of analogs of some nucleoside mono- or diphosphate sugar donors.
Review article and products for sialic acid synthesis and signaling.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service