C4478
S-Gal®/LB Agar Blend
reagent for selection of recombinant bacterial clones
Synonym(s):
Agar Blend
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41106200
NACRES:
NA.85
Recommended Products
grade
for molecular biology
sterility
non-sterile
form
powder
technique(s)
microbiological culture: suitable
suitability
suitable for β-galactosidase test
nonselective for Escherichia coli
nonselective for coliforms
application(s)
food and beverages
microbiology
storage temp.
room temp
Related Categories
General description
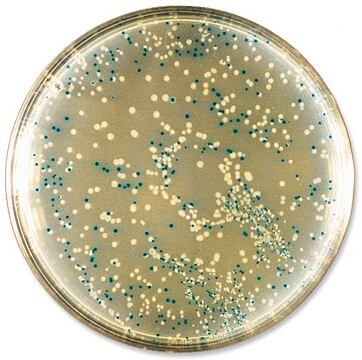
S-Gal® (sodium salt) is an autoclavable, water-soluble, chromogenic substrate for β-galactosidase, used to determine the presence or absence of a cloned DNA insert in bacteria growing on agar plates. S-gal® is designed to replace X-Gal in blue-white selection of recombinant bacterial colonies with the lac+ phenotype.
Application
S-Gal®/LB Agar Blend has been used for the identification of recombinant bacterial colonies.
Suitable for use in selection of recombinant bacterial colonies with the lac+ phenotype. S-Gal® (sodium salt) is water-soluble, autoclavable and can be added to bacterial broth containing agar prior to autoclaving.
Features and Benefits
- More intense color contrast than X-gal
- Water-soluble and autoclavable for easiest use
- Convenient, pre-mixed media
Components
Ingredients (g/L)
Tryptone, 10
Yeast extract, 5
Sodium chloride, 10
Agar, 12
S-Gal, 0.3
Ferric ammonium citrate, 0.5
IPTG, 0.03
Tryptone, 10
Yeast extract, 5
Sodium chloride, 10
Agar, 12
S-Gal, 0.3
Ferric ammonium citrate, 0.5
IPTG, 0.03
Principle
When S-Gal® is cleaved by β-galactosidase, the resulting product will chelate ferric ion to create a black, insoluble precipitate. Lac+ colonies grown in the presence of S-Gal® and ferric ion turn an intense black color, allowing for easy differentiation between lac+ and lac- colonies.
Preparation Note
Suspend contents of one packet in 500 ml distilled or deionized water. Sterilize by autoclaving for 15 to 20 minutes at 121-124°C. For microwaving, heat suspended mix until initial boiling. Mix well. Heat for short intervals with mixing until agar component is in solution. Do not allow boiling for extended periods of time. Antibiotics should be added following autoclaving or microwaving, after cooling to 48-52°C.
Other Notes
The ferric or Fe3+ ion is required for color development and must be added to any S-Gal®
formulation. A medium prepared with S-Gal® is moderately dark due to the presence of ferric ammonium citrate. This darker background often provides enhanced contrast for automated colony counting or isolation.
formulation. A medium prepared with S-Gal® is moderately dark due to the presence of ferric ammonium citrate. This darker background often provides enhanced contrast for automated colony counting or isolation.
Legal Information
S-GAL is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
K Heuermann et al.
BioTechniques, 30(5), 1142-1147 (2001-05-18)
Blue/white selection is the standard method for detecting a cloned DNA fragment. In the absence of an insert, uninterrupted expression of the vector-encoded alpha-complement of beta-galactosidase (beta-gal), results in the hydrolysis of X-gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-beta-D-galactoside) and the subsequent blue staining of
Differential expression of alphaB-crystallin and Hsp27-1 in anaplastic thyroid carcinomas because of tumor-specific alphaB-crystallin gene (CRYAB) silencing
Mineva I, et al.
Cell Stress & Chaperones, 10(3), 171-171 (2005)
N Martin Young et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 277(45), 42530-42539 (2002-08-21)
Mass spectrometry investigations of partially purified Campylobacter jejuni protein PEB3 showed it to be partially modified with an Asn-linked glycan with a mass of 1406 Da and composed of one hexose, five N-acetylhexosamines and a species of mass 228 Da
Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) subtype expression in neuroendocrine tissue and identification of a neuroendocrine tumour-specific Hsp70 truncation.
Zierhut B, et al.
Endocrine-related cancer, 11(2), 377-389 (2004)
John Kelly et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 188(7), 2427-2434 (2006-03-21)
In eukaryotes, N-linked protein glycosylation is a universal modification involving addition of preformed oligosaccharides to select Asn-Xaa-Ser/Thr motifs and influencing multiple biological events. We recently demonstrated that Campylobacter jejuni is the first member of the Bacteria to possess an N-linked
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service