38429
Laccase from Trametes versicolor
powder, light brown, ≥0.5 U/mg
Synonym(s):
Oxygen oxidoreductase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
CAS Number:
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
form
powder
Quality Level
specific activity
≥0.5 U/mg
greener alternative product characteristics
Waste Prevention
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
color
light brown
greener alternative category
storage temp.
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C9H13NO/c1-4-10-7(2)5-9(6-11)8(10)3/h5-6H,4H2,1-3H3
InChI key
NWDZDFOKSUDVJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Laccase is an enzyme, produced by ericoid mycorrhiza and ectomycorrhiza fungi. It belongs to the group of polyphenol oxidases. Laccase is also present in plants and bacteria.
We are committed to bringing you Greener Alternative Products, which adhere to one or more of The 12 Principles of Greener Chemistry. This product has been enhanced for energy efficiency and waste prevention when used in fuel cell and cellulosic ethanol research. For more information see the article in biofiles and Enzymes for Alternative Energy Research.
Application
Laccase from Trametes versicolor has been used:
- to assess the use of four laccase-producing strains in waste water treatment
- in laccase assay
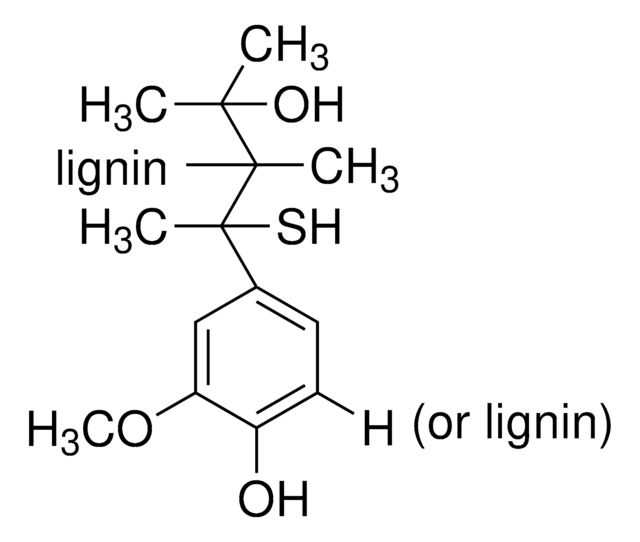
- in screening the lignols
Biochem/physiol Actions
Some of the enzymatic actions of laccase are associated with sporulation, detoxification, morphogenesis, melanin polymerization and it offers protection to spore coat. Laccase can catalyse a number of substrates including medicinal drugs and halogenated pesticides. It utilizes oxygen for its catalysis. For these reasons, it might be useful in the biological degradation of micropollutants in wastewater treatment.
Laccase catalyzes the oxidation of phenol containing compounds, including lignin, through the reduction of oxygen to water. The presence of mediators will allow the oxidation of non-phenlic compounds as well. The primary function of laccase is to degrade lignin in fungi.
Unit Definition
One unit corresponds to the amount of enzyme which converts 1 μmole of catechol per minute at pH 5.0 and 25 °C
Other Notes
former nomenclature: Coriolus versicolor
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Jonas Margot et al.
AMB Express, 3(1), 63-63 (2013-10-25)
Relatively high concentrations of micropollutants in municipal wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) effluents underscore the necessity to develop additional treatment steps prior to discharge of treated wastewater. Microorganisms that produce unspecific oxidative enzymes such as laccases are a potential means to
Laccase-mediator catalyzed conversion of model lignin compounds
Rich JO, et al.
Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol., ACS Symp.Ser., 5, 111-115 (2016)
Laccases and other polyphenol oxidases in ecto-and ericoid mycorrhizal fungi
Burke R and Cairney J
Mycorrhiza, 12(3), 105-116 (2002)
Komal Agrawal et al.
Heliyon, 6(5), e03972-e03972 (2020-05-22)
Multicopper oxidases (MCOs) has a unique feature of having the presence of four Cu atoms arranged into three (Type I, II and III) spectral classification. MCOs laccase due to its broad range of substrate specificity has numerous biotechnological applications. The
Qimiao Shao et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 287(17), 14270-14279 (2012-03-01)
Many insects eat the green leaves of plants but excrete black feces in an as yet unknown mechanism. Insects cannot avoid ingesting pathogens with food that will be specifically detected by the midgut immune system. However, just as in mammals
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service