S7847
CpGenome Turbo Bisulfite Modification Kit
The CpGenome Turbo Bisulfite Modification Kit is designed to simplify & streamline the bisulfite modification process. In just 90 minutes go from DNA sample to bisulfite converted DNA ready for analysis.
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12161503
eCl@ss:
32161000
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
Quality Level
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
CpGenome
application(s)
genomic analysis
shipped in
ambient
Related Categories
General description
Methylation of cytosines located 5′ to guanosine is known to have a profound effect on the expression of many eukaryotic genes. In normal cells methylation occurs predominantly in CG-poor regions, while CG-rich areas, called CpG-islands remain unmethylated. The exceptions are the extensive methylation of CpG islands associated with transcriptional inactivation of regulatory regions of imprinted genes and genes on the inactive X-chromosome of females. Aberrant methylation of normally unmethylated CpG islands has been documented as a relatively frequent event in immortalized and transformed cells and has been associated with transcriptional inactivation of defined tumor suppressor genes in human cancers.
Several methods have been developed to determine the methylation status of cytosine. These include the use of antibodies or protein methyl binding domains, digestion with methylation sensitive, insensitive, or dependent restriction enzymes as in restriction landmark genomic scanning (RLGS), oligonucleotide array hybridization, bisulfite genomic DNA sequencing and Methylation Specific PCR (MSP).
Genomic DNA sequencing, although time consuming and labor intensive, offers a more universal detection method. MSP is an established technology for the monitoring of abnormal gene methylation in selected gene sequences. Utilizing small amounts of DNA, this procedure offers sensitive and specific detection of 5-methylcytosine in promoters. It is being exploited to define tumor suppressor gene function, and to provide a new strategy for early tumor detection by interrogating DNA derived from tissues and bodily fluids.
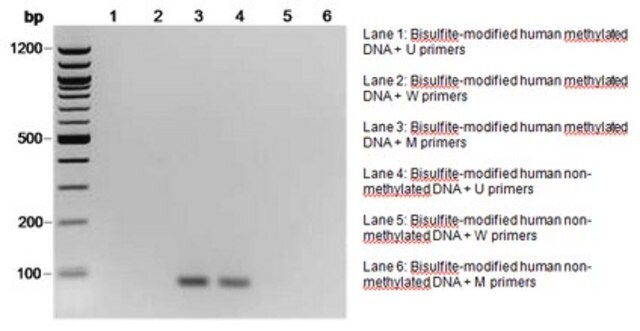
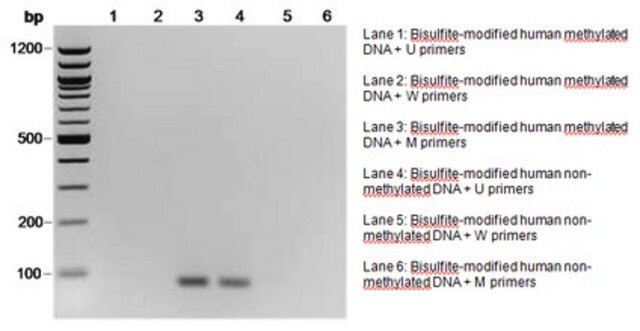
The initial step of both bisulfite genomic sequencing and MSP is to perform a bisulfite modification of the DNA sample. In the bisulfite reaction, all unmethylated cytosines are deaminated and sulfonated, converting them to uracils, while 5-methylcytosines remain unaltered. Thus, the sequence of the treated DNA will differ depending on whether the DNA is originally methylated or unmethylated. Also, the initially complementary DNA strands will no longer be complementary after cytosine conversion. Primers for use in MSP can be designed to specifically amplify either a bisulfite-sensitive, unmethylated strand or a bisulfite-resistant, methylated strand, based upon these chemically-induced differences. Millipore offers a selection of CpG Wiz MSP kits to enable gene-specific analysis by MSP. To learn more about CpG Wiz kits and MSP technology Click here
Several methods have been developed to determine the methylation status of cytosine. These include the use of antibodies or protein methyl binding domains, digestion with methylation sensitive, insensitive, or dependent restriction enzymes as in restriction landmark genomic scanning (RLGS), oligonucleotide array hybridization, bisulfite genomic DNA sequencing and Methylation Specific PCR (MSP).
Genomic DNA sequencing, although time consuming and labor intensive, offers a more universal detection method. MSP is an established technology for the monitoring of abnormal gene methylation in selected gene sequences. Utilizing small amounts of DNA, this procedure offers sensitive and specific detection of 5-methylcytosine in promoters. It is being exploited to define tumor suppressor gene function, and to provide a new strategy for early tumor detection by interrogating DNA derived from tissues and bodily fluids.
The initial step of both bisulfite genomic sequencing and MSP is to perform a bisulfite modification of the DNA sample. In the bisulfite reaction, all unmethylated cytosines are deaminated and sulfonated, converting them to uracils, while 5-methylcytosines remain unaltered. Thus, the sequence of the treated DNA will differ depending on whether the DNA is originally methylated or unmethylated. Also, the initially complementary DNA strands will no longer be complementary after cytosine conversion. Primers for use in MSP can be designed to specifically amplify either a bisulfite-sensitive, unmethylated strand or a bisulfite-resistant, methylated strand, based upon these chemically-induced differences. Millipore offers a selection of CpG Wiz MSP kits to enable gene-specific analysis by MSP. To learn more about CpG Wiz kits and MSP technology Click here
The CpGenome Turbo Bisulfite Modification Kit is designed to simplify and streamline the bisulfite modification process. This kit contains all key reagents for bisulfite modification to allow for the recovery of modified DNA in about 90 minutes as compared to 3-16 hours for similar kits. This rapid, but effective approach employs a proprietary mixture of modification reagents to permit shorter conversion times. This unique mixture of reagents allows for complete conversion of unmethylated cytosines while minimizing damage to the input DNA. After modification, and desulfonation, the modifed DNA is purified and eluted using the provided spin columns resulting in purified, bisulfite-modifed DNA that is ready to use in a wide variety of downstream applications.
Key Features
Key Features
- Input sample to modified DNA in 90 minutes
- Conversion efficiencies of 99.9%
- Effective with as little as 1 ng input DNA
- Recover modified DNA in as little as 25 microliters
- Proven performance in multiple downstream applications
Application
For MSP primer design, please use the MethPrime software package. Click here
Research Category
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Components
Bisulfite Conversion Reagent 1
Bisulfite Conversion Reagent 2
Bisulfite Reagent Diluent
DNA Binding Buffer
Wash Buffer NT3 (Concentrate)*
Elution Buffer NE
Modified DNA Purification Columns
2 mL Collection Tubes
*DNA Wash Buffer requires the addition of 100% Ethanol
Bisulfite Conversion Reagent 2
Bisulfite Reagent Diluent
DNA Binding Buffer
Wash Buffer NT3 (Concentrate)*
Elution Buffer NE
Modified DNA Purification Columns
2 mL Collection Tubes
*DNA Wash Buffer requires the addition of 100% Ethanol
Legal Information
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Dam. 1 - Met. Corr. 1 - Skin Corr. 1C
Supplementary Hazards
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Zhentao Yang et al.
Cell reports, 19(9), 1846-1857 (2017-06-01)
2-hydroxyglutarate-(2-HG)-mediated inhibition of TET2 activity influences DNA hypermethylation in cells harboring mutations of isocitrate dehydrogenases 1 and 2 (IDH1/2). Here, we show that 2-HG also regulates DNA methylation mediated by DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1). DNMT1-dependent hypermethylation of the RIP3 promoter
Characterization of induced tissue-specific stem cells from pancreas by a synthetic self-replicative RNA.
Miyagi-Shiohira, C; Nakashima, Y; Kobayashi, N; Saitoh, I; Watanabe, M; Noguchi, H
Scientific Reports null
Hernán G Hernández et al.
BioTechniques, 55(4), 181-197 (2013-10-11)
Comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation patterns is critical for understanding the molecular basis of many human diseases. While hundreds of PCR-based DNA methylation studies are published every year, the selection and implementation of appropriate methods for these studies can be
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service