479624
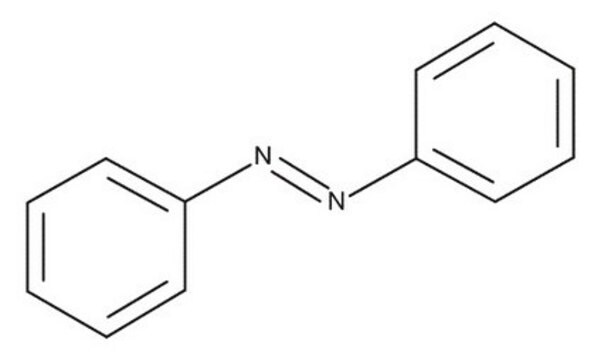
4-(Phenylazo)benzoic acid
98%
Synonym(s):
4-(2-Phenyldiazenyl)benzoic acid, 4-Carboxyazobenzene, Azobenzene-4-carboxylic acid, Azoic acid, p-Phenylazobenzoic acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
C6H5N=NC6H4CO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
226.23
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
mp
247-250 °C (lit.)
functional group
carboxylic acid
SMILES string
OC(=O)c1ccc(cc1)\N=N\c2ccccc2
InChI
1S/C13H10N2O2/c16-13(17)10-6-8-12(9-7-10)15-14-11-4-2-1-3-5-11/h1-9H,(H,16,17)/b15-14+
InChI key
CSPTZWQFHBVOLO-CCEZHUSRSA-N
Related Categories
General description
4-(Phenylazo)benzoic acid (PABA), an azobenzene derivative, is a photo-isomerisable molecule. It can be synthesized by reacting p-aminobenzoic acid with nitrosobenzene. The interaction of PABA with TiO2 and ZnO electrodes has been investigated. A photoreversible switch has been developed using dimethylamino calix[4]arene and PABA. The post functionalization of poly(hydroxyethyl acrylate) core cross-linked star polymers with PABA induces an ability to complex with α-cyclodextrin.
Application
4-(Phenylazo)benzoic acid may be used in the preparation of a novel photochromic ZrO2 precursor solution.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
New dyes for solar cells based on nanostructured semiconducting metal oxides: Synthesis and characterisation of ruthenium (II) complexes with thiol-substituted ligands.
Ohlsson J, et al.
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 148(1), 41-48 (2002)
Synthesis of a new photochromic ZrO2 precursor for preparation of functional thin films.
Nishizawa K, et al.
Key Engineering Materials, 320, 175- 178 (2006)
Chao Luo et al.
Advanced materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla.), 30(23), e1706498-e1706498 (2018-04-25)
Organic compounds are desirable alternatives for sustainable lithium-ion battery electrodes. However, the electrochemical properties of state-of-the-art organic electrodes are still worse than commercial inorganic counterparts. Here, a new chemistry is reported based on the electrochemical conversion of nitro compounds to
Azobenzene-Functionalised Core Cross-Linked Star Polymers and their Host-Guest Interactions.
Tan S, et al.
Australian Journal of Chemistry, 67(1), 173-178 (2014)
A photoresponsive wettability switch based on a dimethylamino Calix[4]arene.
Zhang X, et al.
Chemistry (Weinheim An Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 20(30), 9367-9371 (2014)
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 479624-1G | 4061825766249 |
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service
![4-[4-(Dimethylamino)phenylazo]benzoic acid N-succinimidyl ester ≥98.0% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/120/235/500b5276-3ce2-43b7-9588-3883f13d4ff7/640/500b5276-3ce2-43b7-9588-3883f13d4ff7.png)