S0819
Anti-Sodium Channel NaV1.5 antibody produced in rabbit
affinity isolated antibody, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Anti-SKM2, Anti-Scn5a
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
lyophilized powder
species reactivity
rat
technique(s)
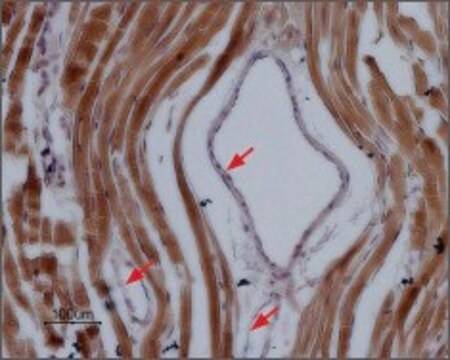
western blot: 1:200 using rat heart membranes
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... SCN5A(6331)
mouse ... Scn5a(20271)
rat ... Scn5a(25665)
General description
SCN5A (sodium voltage-gated channel α subunit 5) codes for an α subunit of the cardiac sodium channel (NaV1.5). It is located on human chromosome 3p22.2.
Immunogen
peptide corresponding to amino acid residues 493-511 of rH1 (Accession P15389). This epitope is identical in mouse and highly homologous in human (17/19 residues identical).
Application
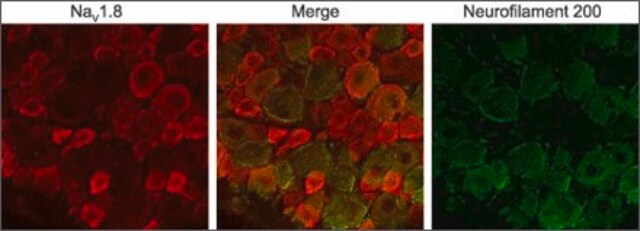
Anti-Sodium Channel NaV1.5 antibody produced in rabbit has been in immunoblotting and immunofluorescence.
Biochem/physiol Actions
SCN5A (sodium voltage-gated channel α subunit 5) regulates the movement of sodium ions into cells, which helps in the production and diffusion of electrical impulses. SCN5A mutations results in the loss or gain of sodium channel activity and cause several cardiac diseases like Brugada syndrome, Long QT syndrome type 3, Sick sinus syndrome and progressive familial heart block.
Physical form
Lyophilized at ~0.8 mg/mL in phosphate buffered, pH 7.4, containing 1% bovine serum albumin, and 0.05% sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Na v1.4 and Na v1.5 are modulated differently during muscle immobilization and contractile phenotype conversion
Rannou F, et al.
Journal of Applied Physiology, 111(2), 495-507 (2011)
Selective Connexin43 Inhibition Prevents Isoproterenol-Induced Arrhythmias and Lethality in Muscular Dystrophy Mice
Gonzalez JP, et al.
Scientific Reports, 5 (2015)
Hiroki Takanari et al.
Cardiovascular research, 111(4), 410-421 (2016-07-01)
In healthy hearts, ventricular gap junctions are mainly composed by connexin43 (Cx43) and localize in the intercalated disc, enabling appropriate electrical coupling. In diseased hearts, Cx43 is heterogeneously down-regulated, whereas activity of calmodulin/calcium-calmodulin protein kinase II (CaM/CaMKII) signalling increases. It
Liang Guo et al.
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology, 123(1), 281-289 (2011-06-23)
Improved in vitro systems for predicting drug-induced toxicity are needed in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries to decrease late-stage drug attrition. One unmet need is an early screen for cardiotoxicity, which accounts for about one third of safety-based withdrawn pharmaceuticals.
Exome Sequencing Identifies Compound Heterozygous Mutations in SCN5A Associated with Congenital Complete Heart Block in the Thai Population
Thongnak C, et al.
Disease Markers (2016)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service