CN354-05
Canine Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells: CnAOSMC (Cryovial)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
canine aorta (normal, tunica intima and media)
packaging
pkg of 500,000 cells
manufacturer/tradename
Cell Applications, Inc
growth mode
Adherent
karyotype
2n = 78
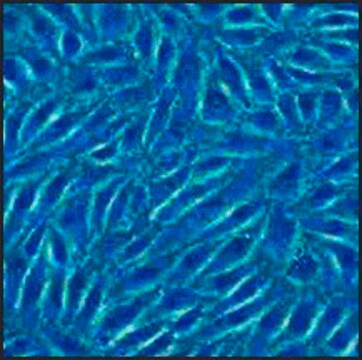
morphology
smooth muscle
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
relevant disease(s)
cardiovascular diseases
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−196°C
General description
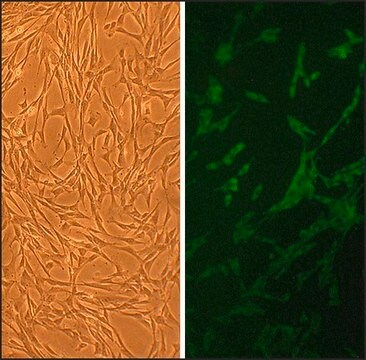
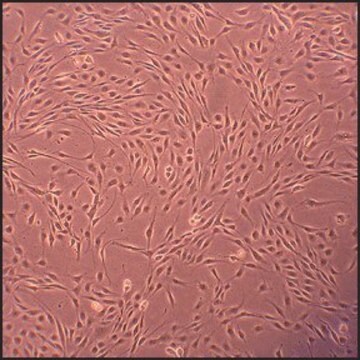
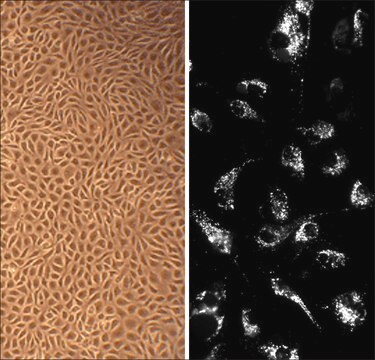
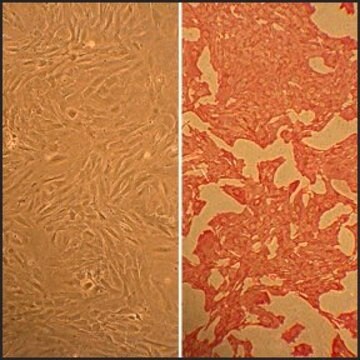
Canine Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells (CnAOSMC) are derived from tunica intima and tunica media of normal canine aorta. They are cryopreserved at second passage and can be cultured and propagated at least 10 population doublings. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is a potent mitogen and chemotactic agent which may be involved in intimal hyperplasia and atherosclerosis. It was shown that significant regional difference in PDGF production in normal canine aorta, and that SMC are a significant contributor to the regional variation in PDGF production.
1. It was also shown that nebivolol relaxes vascular smooth muscle by NO- and cyclic GMP-dependent mechanisms.
2. Graft SMCs are functionally altered producing more platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) than aortic SMCs. PDGF produced by graft SMCs may contribute to the development of intimal hyperplasia.
3. Graft SMCs have decreased proliferation response, but have similar migratory response to PDGF compared with aortic SMCs.
4. Intrinsic differences in endothelial cells from proximal aorta versus the distal aorta have different capacity to produce PDGF in response to stimulants whereas unstimulated SMCs did not exhibit regional variation in PDGF production and did not increase PDGF secretion after PMA or thrombin treatment.
5. Identification of the cDNA for canine isoform of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) can be used in the study of allograft rejection and cardiovascular disease.
RECENT PUBLICATIONS Kiyan, Y., S. Tkachuk, D. Hilfker-Kleiner, H. Haller, B. Fuhrman, and Inna Dumler. 2014. oxLDL induces inflammatory responses in vascular smooth muscle cells via urokinase receptor association with CD36 and TLR4. J Molec and Cell Cardiol, 66:72-82.
Ignarro, L.J. et al, Nitric Oxide. 7(2):75-82 (2002).
Madura, J.A. et al, J. Vas Res. 33(1):53-61 (1996).
Pitsch, R.J. et al, J. Vasc. Surg. 26(1):70-8 (1997).
Minion, D.J. et al, J. Vasc. Surg. 31(5):953-9 (2000).
Van Aalst, J.A. et al, J. Vasc. Surg. 32(3):584-92 (2000).
Wang, X. et al, Am. J. Physiol. 275(4 Pt 2):H1122-9 (1998).
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Cell Line Origin
Application
Components
Preparation Note
- 2nd passage, >500,000 cells in Canine Smooth Muscle Cell Basal Medium containing 10% FBS & 10% DMSO
- Can be cultured at least 10 doublings
Subculture Routine
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Protocols
Technical information for working with Canine Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells including thawing, subculturing and cryopreservation
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service