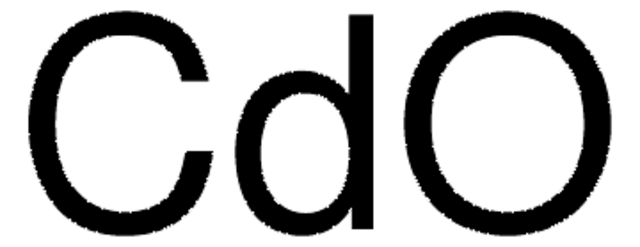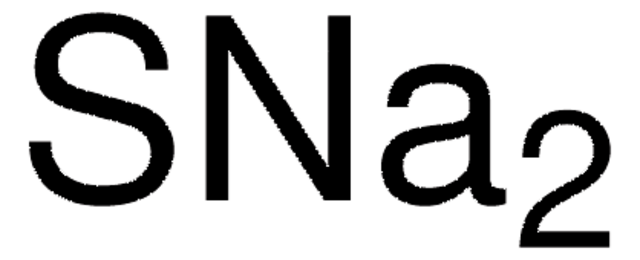About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor density
8.9 (vs air)
vapor pressure
1 mmHg ( 183.8 °C)
10 mmHg ( 246 °C)
grade
purum p.a.
Assay
≥99% (T)
form
powder
autoignition temp.
450 °F
resistivity
2E23 μΩ-cm, 20°C
ign. residue
≤0.2%
bp
444.7 °C (lit.)
mp
112.8 °C (rhombic) (lit.)
117-120 °C (lit.)
119.0 °C (monoclinic) (lit.)
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 mg/kg
sulfate (SO42-): ≤50 mg/kg
cation traces
Ca: ≤50 mg/kg
Cd: ≤50 mg/kg
Co: ≤50 mg/kg
Cu: ≤50 mg/kg
Fe: ≤50 mg/kg
K: ≤100 mg/kg
Na: ≤100 mg/kg
Ni: ≤50 mg/kg
Pb: ≤50 mg/kg
Zn: ≤50 mg/kg
SMILES string
[S]
InChI
1S/S
InChI key
NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
4.1B - Flammable solid hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service