AX90010TC
AXIS™ Axon Isolation Device, 900 µm
The AXIS Axon Isolation Devices have been shown to effectively isolate cell bodies from differentiating neurites for a variety of cell types.
Synonym(s):
AXIS™ Axon Investigation Platform
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41104923
eCl@ss:
32011202
Recommended Products
material
polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)
manufacturer/tradename
AXIS™
technique(s)
cell based assay: suitable
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
shipped in
ambient
General description
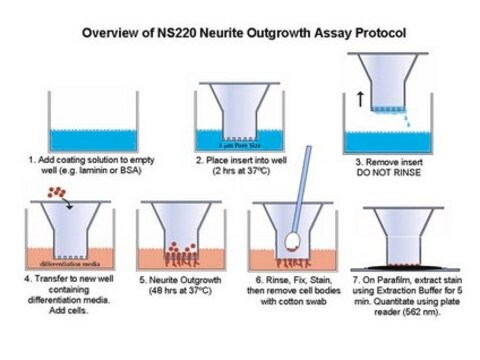
AXIS Axon Isolation Devices are tissue culture ready (TC) microfluidic tools that out-of-the-box enable researchers to easily isolate, observe, and test developing neurites. They are currently being offered in four different formats to provide test flexibility during investigation.
AX90010 consists of 10 units of AX900, an axon isolation device consisting of four wells, two channels, and a set of microgrooves. Two of the wells are interconnected by a channel on each side of the device. The microgrooves are located in the area between the two channels and their length is 900µm. Each microgroove is approximately 5µm in height by 10µm in width and are designed to allow neurite passage to traverse through while preventing cell bodies from flowing across the device. There are roughly 120 microgrooves in each AX900 device.
The AXIS Axon Isolation Devices have been shown to effectively isolate cell bodies from differentiating neurites for a variety of cell types (Taylor et al., 2005; Park et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2008; Yang, et al., 2009; Taylor et al., 2009) and will likely work with most neuronal cell type that can be successfully grown in tissue culture. Because the AXIS devices are made from an inert and non-toxic polymer, cultures grown within AXIS devices can be maintained for weeks at a time. (Chun et al., 1992; Shibayama et al., 1991). In addition, because the polymer used to fabricate the axon isolation devices is optically clear, cells cultured within the device can be imaged with high resolution microscopy, including live cell imaging, confocal, and differential interference microscopy (Taylor et al., 2005; Park et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2008; Yang, et al., 2009; Taylor et al., 2009).
The microfluidic design of the AXIS devices is highly conducive to generation of hydrostatic pressure, which can be selectively used to isolate a solution, as well as chemical targets of interest, on a designated side of the device (Park et al., 2006). In addition, immunocytochemistry (IHC) can also be performed within an AXIS Axon Isolation device and a protocol to do so is provided in the manual.
AX90010 consists of 10 units of AX900, an axon isolation device consisting of four wells, two channels, and a set of microgrooves. Two of the wells are interconnected by a channel on each side of the device. The microgrooves are located in the area between the two channels and their length is 900µm. Each microgroove is approximately 5µm in height by 10µm in width and are designed to allow neurite passage to traverse through while preventing cell bodies from flowing across the device. There are roughly 120 microgrooves in each AX900 device.
The AXIS Axon Isolation Devices have been shown to effectively isolate cell bodies from differentiating neurites for a variety of cell types (Taylor et al., 2005; Park et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2008; Yang, et al., 2009; Taylor et al., 2009) and will likely work with most neuronal cell type that can be successfully grown in tissue culture. Because the AXIS devices are made from an inert and non-toxic polymer, cultures grown within AXIS devices can be maintained for weeks at a time. (Chun et al., 1992; Shibayama et al., 1991). In addition, because the polymer used to fabricate the axon isolation devices is optically clear, cells cultured within the device can be imaged with high resolution microscopy, including live cell imaging, confocal, and differential interference microscopy (Taylor et al., 2005; Park et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2008; Yang, et al., 2009; Taylor et al., 2009).
The microfluidic design of the AXIS devices is highly conducive to generation of hydrostatic pressure, which can be selectively used to isolate a solution, as well as chemical targets of interest, on a designated side of the device (Park et al., 2006). In addition, immunocytochemistry (IHC) can also be performed within an AXIS Axon Isolation device and a protocol to do so is provided in the manual.
The development of the vertebrate nervous system entails the generation and differentiation of neurons, establishment of signaling circuits, and the formation of numerous synapses. In particular, the formation of axons and dendrites during differentiation has been an area of intense interest. Although tremendous progress has been made in this area, neuronal outgrowth studies have been hampered by the absence of a solid, easy to use, neurite culturing platform which physically orients the cells during investigation. Traditional outgrowth experiments, conducted either by culturing neural stem cells, primary neurons, or tissue slices, typically result in random, overlapping neurite extensions. The ability to address questions surrounding the specific roles of axons, dendrites and somas in neuron differentiation and growth requires a faster, more specialized method that allows scientists to spatially isolate and study individual neurites and their function. To this end, Millipore now offers its most advanced tool for the isolation, visualization, and characterization of neurite outgrowth, the AXon Investigation System (AXIS). AXIS is a unique, easy to use, slide-mounted microfluidic platform that allows culture, regulation, and directional differentiation of neuronal cells via a system of growth chambers and interconnected channels. AXIS devices physically isolate developing neurites from each other and their respective neural cell bodies. In addition, the use of hydrostatic pressure during analysis provides researchers with an opportunity for targeted exposure of neuronal parts to growth factors, drug compounds, or other reagents of biological interest. This ability to selectively control exposure of neuronal outgrowth makes AXIS a powerful platform for any researcher interested in understanding axons, dendrites, somas, and their roles in synaptic formation, neural cell development, differentiation, regeneration, degeneration, and trauma.
Cell Line Description
Neural Lineage Cells
Application
Research Category
Neuroscience
Neuroscience
The AXIS Axon Isolation Devices have been shown to effectively isolate cell bodies from differentiating neurites for a variety of cell types.
Components
10 devices of AX900
Quality
Each unit is visually inspected to conform with internal specifications for channel width, length, and height.
Storage and Stability
The AXIS devices should be stored at room temperature in a clean dry area away from any chemicals or direct light. When stored properly the devices are stable for 6 months from date of receipt. Discard any remaining reagents after the expiration date.
Legal Information
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service